RNA
messenger RNA (mRNA) see ribonucleic acid.
ribosomal RNA (rRNA) see ribonucleic acid.
transfer RNA (tRNA) see ribonucleic acid.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
trans·fer RNA (tRNA),
short-chain RNA molecules present in cells in at least 20 varieties, each variety is capable of combining with a specific amino acid (see aminoacyl-tRNA). By joining (through their anticodons) with particular spots (codons) along the messenger RNA molecule and carrying their amino acyl residues along, they lead to the formation of protein molecules with a specific amino acid arrangement-the one ultimately dictated by a segment of DNA in the chromosomes. Each tRNA has about 80 nucleotides (MW about 25,000); most of the 20 varieties occur in multiple "isoacceptor" forms, separable by chromatography. Further subvarieties exist in, e.g., different strains of an organism, in subcellular organelles, and in different metabolic states. Cognate tRNAs are the tRNAs recognized by the specific amino acyl-tRNA synthetases.
Synonym(s): acceptor RNA, soluble RNA
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
transfer RNA
n. Abbr. tRNA
One of a class of RNA molecules that transport amino acids to ribosomes for incorporation into a polypeptide undergoing synthesis.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
trans·fer RNA
(tRNA) (trans'fĕr)Short-chain RNA molecules present in cells in at least 20 varieties, each variety capable of combining with a specific amino acid (see aminoacyl-tRNA). By joining (through their anticodons) with particular spots (codons) along the messenger RNA molecule and carrying their amino acyl residues along, they lead to the formation of protein molecules with a specific amino acid arrangement.
Synonym(s): soluble RNA.
Synonym(s): soluble RNA.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
transfer RNA
A short-chain RIBONUCLEIC ACID molecule present in cells in at least 20 different varieties, each capable of combining with a specific amino acid and positioning it appropriately in a polypeptide chain that is being synthesized in a ribosome. Transfer RNA is a four-armed, clover-leaf-like structure. At the end of one arm is an ANTICODON, complementary to the codon for an amino acid in MESSENGER RNA. At the end of the opposite arm is a site to which the appropriate amino acid can be covalently linked. When a molecule of transfer RNA is linked to the amino acid corresponding to its anticodon it becomes aminoacyl-tRNA. The identity of the passenger on a particular tRNA molecule is determined by its anticodon rather than by its attached amino acid.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
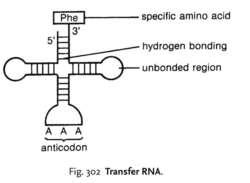
transfer RNA (tRNA)
a form of RNA molecule with about 80 NUCLEOTIDES and a secondary ‘cloverleaf structure, whose function is to carry specific AMINO ACIDS to the ribosomes during TRANSLATION. At one end (3′ end) there is attachment of the amino acid producing AMINOACYL-tRNA. One of the arms of the cloverleaf, the ‘anticodon arm’, contains the anticodon with three bases complementary to the codon on MESSENGER RNA. See Fig. 302 . Different tRNA molecules bind different amino acids and act as adaptors to match the amino acids to their specific codons on mRNA.Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005