thrombus
[throm´bus]a stationary blood clot along the wall of a blood vessel, frequently causing vascular obstruction. Some authorities differentiate thrombus formation from simple coagulation or clot formation. See also embolus.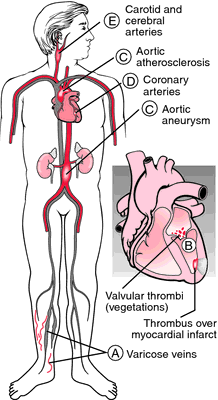

Sites of thrombus formation. From Damjanov, 1996.
mural thrombus one attached to the wall of the heart adjacent to an area of diseased endocardium, or to the aortic wall overlying an intimal lesion. See also parietal thrombus.
occluding thrombus one that occupies the entire lumen of a vessel and obstructs blood flow.
parietal thrombus one attached to a vessel or heart wall; see also mural thrombus.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
mu·ral throm·bus
a thrombus formed on and attached to a diseased patch of endocardium, not on a valve or on one side of a large blood vessel.
See also: parietal thrombus.
See also: parietal thrombus.
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
mu·ral throm·bus
(myū'răl throm'bŭs)A thrombus formed on and attached to a diseased patch of endocardium, not on a valve or on one side of a large blood vessel.
See also: parietal thrombus
See also: parietal thrombus
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
mural thrombus
A blood clot formed within the blood and attached to the wall of a blood vessel or to the lining of a chamber of the heart. Mural thrombi are liable to break loose and form dangerous EMBOLI.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005