mitosis
[mi-to´sis]the ordinary process of cell division resulting in the formation of two daughter cells, by which the body replaces dead cells. The daughter cells have identical diploid complements of chromosomes (46 in human somatic cells). Cell division that results in haploid reproductive cells is known as meiosis. The period between mitotic divisions is called interphase, and mitosis itself occurs in four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. adj., adj mitot´ic.
During interphase the chromosomes are extended long threads that cannot be visibly identified. The DNA of the chromosomes is replicated during this phase, resulting in duplication of the genetic material.
During prophase the chromosomes coil up and contract, becoming short rods. Each chromosome consists of a pair of strands, called chromatids, held together at the centromere. At the same time the nuclear envelope disappears, and the centriole divides and the two daughter centrioles move toward opposite poles of the cell.
During metaphase the chromosomes move so that their centromeres are aligned in the equatorial plane of the cell (the metaphase plate), and the mitotic spindle forms. The mitotic spindle is formed of fibers composed of microtubules, which extend from the centrioles to the metaphase plate and to the centromeres of the chromosomes.
During anaphase the chromatids of each chromosome separate, becoming new daughter chromosomes, which are drawn to opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers.
During telophase the daughter chromosomes arrive at the poles of the cell, where they are surrounded by two new nuclear envelopes as they begin to uncoil and extend. During this phase, cytokinesis, division of the cytoplasm, occurs. A furrow forms around the cell in the equatorial plane and deepens until the two daughter cells are separated.
Originally, the term mitosis referred only to the division of the nucleus, which can occur without cytokinesis in certain fungi and in the fertilized eggs of insects. As used now, it usually refers to mitotic cell division.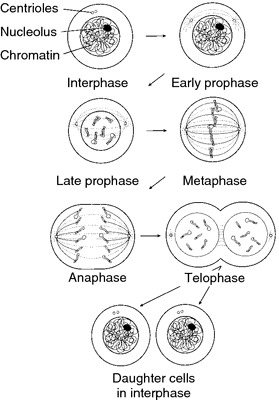
During interphase the chromosomes are extended long threads that cannot be visibly identified. The DNA of the chromosomes is replicated during this phase, resulting in duplication of the genetic material.
During prophase the chromosomes coil up and contract, becoming short rods. Each chromosome consists of a pair of strands, called chromatids, held together at the centromere. At the same time the nuclear envelope disappears, and the centriole divides and the two daughter centrioles move toward opposite poles of the cell.
During metaphase the chromosomes move so that their centromeres are aligned in the equatorial plane of the cell (the metaphase plate), and the mitotic spindle forms. The mitotic spindle is formed of fibers composed of microtubules, which extend from the centrioles to the metaphase plate and to the centromeres of the chromosomes.
During anaphase the chromatids of each chromosome separate, becoming new daughter chromosomes, which are drawn to opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers.
During telophase the daughter chromosomes arrive at the poles of the cell, where they are surrounded by two new nuclear envelopes as they begin to uncoil and extend. During this phase, cytokinesis, division of the cytoplasm, occurs. A furrow forms around the cell in the equatorial plane and deepens until the two daughter cells are separated.
Originally, the term mitosis referred only to the division of the nucleus, which can occur without cytokinesis in certain fungi and in the fertilized eggs of insects. As used now, it usually refers to mitotic cell division.

Mitosis shown as occurring in a cell of a hypothetical animal with a diploid chromosome number of six (haploid number three); one pair of chromosomes is short, one pair is long and hooked, and one pair is long and knobbed. From Dorland's, 2000.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
mi·to·sis
, pl.mi·to·ses
(mī-tō'sis, -sēz),The usual process of somatic reproduction of cells consisting of a sequence of modifications of the nucleus (prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) that result in the formation of two daughter cells with exactly the same chromosome and nuclear DNA content as that of the original cell.
See also: cell cycle.
See also: cell cycle.
Synonym(s): indirect nuclear division, mitotic division
[G. mitos, thread]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
mitosis
(mī-tō′sĭs)n. pl. mito·ses (-sēz) Biology
1. The process in cell division by which the nucleus divides, typically consisting of four stages, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, and normally resulting in two new nuclei, each of which contains a complete copy of the parental chromosomes. Also called karyokinesis.
2. The entire process of cell division including division of the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
mi·tot′ic (-tŏt′ĭk) adj.
mi·tot′i·cal·ly adv.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
mi·to·sis
, pl. mitoses (mī-tō'sis, -sēz)The usual process of somatic reproduction of cells consisting of a sequence of modifications of the nucleus (prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) that result in the formation of two daughter cells with exactly the same chromosome and DNA content as that of the original cell.
See also: cell cycle
Synonym(s): indirect nuclear division.
See also: cell cycle
Synonym(s): indirect nuclear division.
[G. mitos, thread]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
mitosis
The division of a cell nucleus to produce two daughter cells having identical genetic composition to the parent cell. First the long strands of CHROMATIN replicate and coil up to form dense chromosomes with the two copies (chromatids) joined at the CENTROMERE so that they appear X-shaped. At the same time, the envelope of the cell nucleus disrupts (prophase). Then two sets of strand-like microtubules (the spindle) appear, radiating from each end of the cell to the centre, the metaphase plate, and the chromosomes align themselves on the plate with the centromeres at the equator (metaphase). The copies of each chromosome (chromatids) now separate and move to opposite poles of the spindle (anaphase). Finally, the cell separates into two, the chromatin uncoils and the nuclear envelope of each reforms (telophase).Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
mitosis
a type of nuclear division by which two daughter cells are produced from one parent cell, with no change in chromosome number. Mitosis is associated with asexual growth and repair and, although it is a continuous process, has been divided up into four main stages, given below. Further details of each stage can be obtained by referring to individual entries.- PROPHASE: chromosomes contract and become visible as threads. Each chromosome divides into two CHROMATIDS and the nuclear membrane disintegrates.
- METAPHASE: chromosomes migrate to the equator of a spindle and become attached to the spindle microtubes by their CENTROMERES.
- ANAPHASE: chromatids separate and go to opposite poles.
- TELOPHASE: nuclear membrane reforms, chromosomes lengthen and cannot be distinguished. See also MEIOSIS.
Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
mitosis
Process by which a cell nucleus divides into two nuclei with chromosome numbers and genetic make-up identical to that of the parent cell. Mitosis is inhibited by anaesthetics and thus tissue repair is delayed. It is also slowed by hypoxia. Example: the mitosis of the basal cells of the corneal epithelium; the mitosis of the epithelial cells of the crystalline lens adding new cells to it which eventually form new lens fibres. See apoptosis; chromosome; corneal abrasion; Krebs cycle.
Millodot: Dictionary of Optometry and Visual Science, 7th edition. © 2009 Butterworth-Heinemann
mi·to·sis
, pl. mitoses (mī-tō'sis, -sēz)Usual process of somatic reproduction of cells consisting of a sequence of modifications of the nucleus that result in the formation of two daughter cells with exactly the same chromosome and nuclear DNA content as that of the original cell.
[G. mitos, thread]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012