synapse
[sin´aps]the junction between the processes of two neurons or between a neuron and an effector organ, where neural impulses are transmitted by chemical means. The impulse causes the release of a neurotransmitter (e.g., acetylcholine or norepinephrine) from the presynaptic membrane of the axon terminal. The neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft, bind with specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, causing depolarization or hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic cell. See also neuron.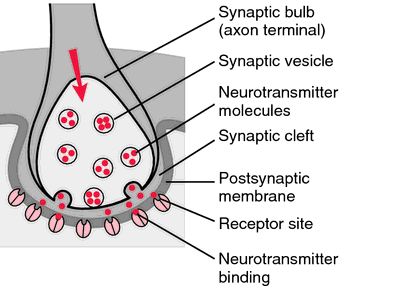

Components of a synapse. From Applegate, 2000.
axoaxonic synapse one between the axon of one neuron and the axon of another neuron.
axodendritic synapse one between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another.
axodendrosomatic synapse one between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites and body of another.
axosomatic synapse one between the axon of one neuron and the body of another.
dendrodendritic synapse one from a dendrite of one cell to a dendrite of another.
electrotonic synapse a special type of gap junction found in tissue such as the myocardium.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
ax·o·so·mat·ic syn·apse
the synaptic junction of an axon terminal of one nerve cell to the cell body of another nerve cell.
Synonym(s): pericorpuscular synapse
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012