vasopressin
[vas″o-pres´in]a hormone secreted by cells of the hypothalamic nuclei and stored in the posterior pituitary for release as necessary; it stimulates contraction of the muscular tissues of the capillaries and arterioles, raising the blood pressure, and increases peristalsis, exerts some influence on the uterus, and influences resorption of water by the kidney tubules, resulting in concentration of urine. Its rate of secretion is regulated chiefly by the osmolarity of the plasma. Also prepared synthetically or obtained from the posterior pituitary of domestic animals; used as an antidiuretic. Called also antidiuretic hormone.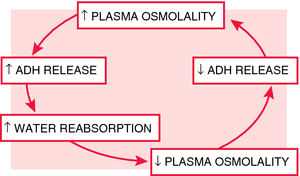

Vasopressin (ADH) regulation. ADH is secreted by the posterior pituitary gland primarily in response to an increase in plasma osmolality. From Malarkey and McMorrow, 2000.
arginine vasopressin vasopressin containing arginine, as that from humans and most other mammals; for medicinal uses, see vasopressin. Called also argipressin.
lysine vasopressin the antidiuretic hormone of the pig family, differing from arginine vasopressin in having lysine instead of arginine at position 8. A synthetic preparation, lypressin, is used as an antidiuretic and vasoconstrictor.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
ar·gi·nine va·so·pres·sin (AVP),
[MIM*192340]vasopressin containing an arginyl residue in position 8 (as in chickens and most mammals, including humans); porcine vasopressin has a lysyl residue at position 8. All are vasopressors.
Synonym(s): argipressin
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
arginine vasopressin
ADH-antidiuretic hormone, see there.McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
ar·gi·nine va·so·pres·sin
(AVP) (ahr'ji-nēn vā'sō-pres'in)This agent contains an arginyl residue in position 8 (as in chickens and most mammals, including humans); porcine vasopressin has a lysyl residue at position 8. All are vasopressors.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
arginine vasopressin
VASOPRESSIN, one of the two hormones from the rear lobe of the PITUITARY GLAND. The antidiuretic hormone in humans.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005