cavity
[kav´ĭ-te]1. a hollow or space, or a potential space, within the body or one of its organs; called also caverna and cavum.
2. the lesion produced by dental caries.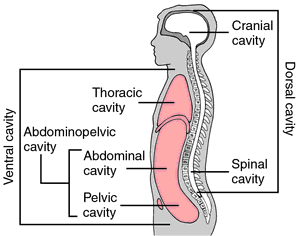

Cavities in the body. From Applegate, 2000.
abdominal cavity the cavity of the body between the diaphragm above and the pelvis below, containing the abdominal organs.
absorption c's cavities in developing compact bone due to osteoclastic erosion, usually occurring in the areas laid down first.
amniotic cavity the closed sac between the embryo and the amnion, containing the amniotic fluid.
cranial cavity the space enclosed by the bones of the cranium.
glenoid cavity a depression in the lateral angle of the scapula for articulation with the humerus.
marrow cavity (medullary cavity) the cavity that contains bone marrow in the diaphysis of a long bone; called also medullary canal.
nasal cavity the proximal portion of the passages of the respiratory system, extending from the nares to the pharynx; it is divided into left and right halves by the nasal septum and is separated from the oral cavity by the hard palate.
oral cavity the cavity of the mouth, bounded by the jaw bones and associated structures (muscles and mucosa).
pelvic cavity the space within the walls of the pelvis.
pericardial cavity the potential space between the epicardium and the parietal layer of the serous pericardium.
peritoneal cavity the potential space between the parietal and the visceral peritoneum.
pleural cavity the potential space between the two layers of pleura.
pulp cavity the pulp-filled central chamber in the crown of a tooth.
cavity of septum pellucidum the median cleft between the two laminae of the septum pellucidum. Called also pseudocele, pseudocoele, and fifth ventricle.
serous cavity a coelomic cavity, like that enclosed by the pericardium, peritoneum, or pleura, not communicating with the outside of the body and lined with a serous membrane, i.e., one which secretes a serous fluid.
tension cavity cavities of the lung in which the air pressure is greater than that of the atmosphere.
thoracic cavity the portion of the ventral body cavity situated between the neck and the diaphragm; it contains the pleural cavity.
tympanic cavity the major portion of the middle ear, consisting of a narrow air-filled cavity in the temporal bone that contains the auditory ossicles and communicates with the mastoid air cells and the mastoid antrum by means of the aditus and the nasopharynx by means of the auditory tube. The middle ear and the tympanic cavity were formerly regarded as being synonymous.
uterine cavity the flattened space within the uterus communicating proximally on either side with the fallopian tubes and below with the vagina.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
tho·rac·ic cav·i·ty
[TA]the space within the thoracic walls, bounded below by the diaphragm and above by the base of the neck or superior thoracic aperture.
Synonym(s): cavitas thoracica/thoracis [TA], cavum thoracis
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
tho·rac·ic cav·i·ty
(thōr-as'ik kav'i-tē) [TA]The space within the thoracic walls, bounded below by the diaphragm and above by the neck.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
thoracic cavity
the space within the THORAX.Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005