retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)
A brown monolayer of cells of the retina situated next to the choroid composed of cells joined by tight junctions and filled with pigment, mainly melanin and lipofuscin (Fig. R9). Depending upon the amount of pigment, the fundus will appear dark or light. The main functions of the RPE are: control of the flow of fluid and nutrients entering the retina (blood-retina barrier), absorption of scattered light, visual pigment metabolism, vitamin A metabolism which contributes to visual pigment regeneration, ingestion and digestion of photoreceptor discs (phagocytosis), retinal adhesion and synthesis of growth factors of adjacent tissues. A dysfunction of this tissue can be detected with the electrooculogram. See Bruch's membrane; Usher's syndrome.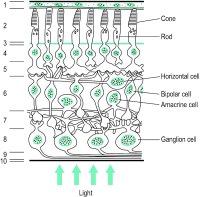


Fig. R9 Schematic representation of the cells and layers of the central primate retina (1: retinal pigment epithelium; 2: layer of rods and cones; 3: external limiting membrane; 4: outer nuclear layer; 5: outer plexiform layer; 6: inner nuclear layer; 7: inner plexiform layer; 8: ganglion cell layer; 9: nerve fibre layer; 10: internal limiting membrane)
Millodot: Dictionary of Optometry and Visual Science, 7th edition. © 2009 Butterworth-Heinemann