glutamic acid
[gloo-tam´ik]a dibasic amino acid, one of the nonessential amino acids; it is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Its hydrochloride salt is used as a gastric acidifier. See also monosodium glutamate.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
glu·tam·ic ac·id (E, Glu),
(glū-tam'ik as'id),An amino acid; the sodium salt is monosodium glutamate. Compare: glutamate.
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
glutamic acid
(glo͞o-tăm′ĭk)n.
A nonessential amino acid, C5H9NO4, occurring widely in plant and animal tissue and proteins, and having monosodium glutamate as a salt.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
glu·tam·ic ac·id
(E) (glū-tam'ik as'id)An amino acid that occurs in proteins; the sodium salt is monosodium glutamate.
Compare: glutamate
Compare: glutamate
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
glutamic acid
Glutamate, an AMINO ACID present in most proteins. One of its salts, MONOSODIUM GLUTAMATE, is widely used as a seasoning and flavouring agent and has been suspected as the cause of the CHINESE RESTAURANT SYNDROME.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
glutamic acid (E, Glu)
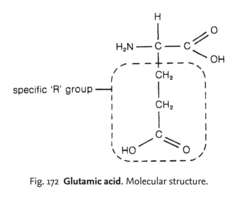
one of 20 AMINO ACIDS common in proteins that has an extra carboxyl group and is acidic in solution. See Fig. 172 . The ISOELECTRIC POINT of glutamic acid is 3.2.Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
glu·tam·ic acid
(glū-tam'ik as'id)An amino acid; the sodium salt is monosodium glutamate.
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012