gland
[gland]an aggregation of cells specialized to secrete or excrete materials not related to their ordinary metabolic needs. Glands are divided into two main groups, endocrine and exocrine. adj., adj glan´dular.
The endocrine glands, or ductless glands, discharge their secretions (hormones) directly into the blood; they include the adrenal, pituitary, thyroid, and parathyroid glands, the islands of Langerhans in the pancreas, the gonads, the thymus, and the pineal body. The exocrine glands discharge through ducts opening on an external or internal surface of the body; they include the salivary, sebaceous, and sweat glands, the liver, the gastric glands, the pancreas, the intestinal, mammary, and lacrimal glands, and the prostate. The lymph nodes are sometimes called lymph glands but are not glands in the usual sense.
The endocrine glands, or ductless glands, discharge their secretions (hormones) directly into the blood; they include the adrenal, pituitary, thyroid, and parathyroid glands, the islands of Langerhans in the pancreas, the gonads, the thymus, and the pineal body. The exocrine glands discharge through ducts opening on an external or internal surface of the body; they include the salivary, sebaceous, and sweat glands, the liver, the gastric glands, the pancreas, the intestinal, mammary, and lacrimal glands, and the prostate. The lymph nodes are sometimes called lymph glands but are not glands in the usual sense.

Classification of glands according to mode of secretion. From Applegate, 2000.
acinous gland one made up of one or more acini (oval or spherical sacs).
adrenal gland see adrenal gland.
apocrine gland one whose discharged secretion contains part of the secreting cells.
areolar g's Montgomery's glands.
axillary g's lymph nodes in the axilla.
Bartholin g's two small mucus-secreting glands, one on each side in the lower pole of the labium majus and connected to the surface by a duct lined with transitional cells, which opens just external to the hymenal ring. Their exact function is not clear but they are believed to secrete mucus to moisten the vestibule during sexual excitement. Called also major vestibular glands.
Bowman's g's olfactory glands.
bronchial g's seromucous glands in the mucosa and submucosa of the bronchial walls.
Brunner's g's glands in the submucosa of the duodenum that secrete intestinal juice; called also duodenal glands.
buccal g's seromucous glands on the inner surface of the cheeks; called also genal glands.
bulbocavernous g's (bulbourethral g's) two glands embedded in the substance of the sphincter of the male urethra, posterior to the membranous part of the urethra; their secretion lubricates the urethra; called also Cowper's glands.
cardiac g's mucus-secreting glands of the cardiac part (cardia) of the stomach.
celiac g's lymph nodes anterior to the abdominal aorta.
ceruminous g's cerumin-secreting glands in the skin of the external auditory canal.
cervical g's
1. the lymph nodes of the neck.
2. compound clefts in the wall of the uterine cervix.
ciliary g's sweat glands that have become arrested in their development, situated at the edges of the eyelids; called also Moll's glands.
circumanal g's specialized sweat and sebaceous glands around the anus; called also Gay's glands.
Cobelli's g's mucous glands in the esophageal mucosa just above the cardia.
coccygeal gland glomus coccygeum.
compound gland one made up of a number of smaller units whose excretory ducts combine to form ducts of progressively higher order.
Cowper's g's bulbourethral glands.
ductless g's endocrine glands.
duodenal g's Brunner's glands.
Ebner's g's serous glands at the back of the tongue near the taste buds.
eccrine gland one of the ordinary or simple sweat glands, which are of the merocrine type.
endocrine g's see endocrine glands.
exocrine g's glands that discharge their secretions through ducts opening on internal or external surfaces of the body; see gland.
fundic g's (fundus g's) numerous tubular glands in the mucosa of the fundus and body of the stomach that contain the cells that produce acid and pepsin.
gastric g's the secreting glands of the stomach, including the fundic, cardiac, and pyloric glands.
Gay's g's circumanal glands.
genal g's buccal glands.
glossopalatine g's mucous glands at the posterior end of the smaller sublingual glands.
haversian g's synovial villi.
holocrine gland one whose discharged secretion contains the entire secreting cells.
intestinal g's straight tubular glands in the mucous membrane of the intestines, in the small intestine opening between the bases of the villi, and containing argentaffin cells. Called also crypts or glands of Lieberkühn.
jugular gland a lymph node behind the clavicular insertion of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Krause's gland an accessory lacrimal gland deep in the conjunctival connective tissue, mainly near the upper fornix.
lacrimal g's the glands that secrete tears; see also lacrimal apparatus.
g's of Lieberkühn intestinal glands.
lingual g's the seromucous glands on the surface of the tongue.
lingual g's, anterior seromucous glands near the apex of the tongue.
Littre's g's
1. preputial glands.
2. the male urethral glands.
lymph gland lymph node.
major vestibular g's Bartholin glands.
mammary gland a specialized gland of the skin of female mammals, which secretes milk for the nourishment of their young; it exists in a rudimentary state in the male. See also breast.
meibomian g's sebaceous follicles between the cartilage and conjunctiva of the eyelids. Called also tarsal glands.
merocrine gland one whose discharged secretion contains no part of the secreting cells.
mixed g's
1. seromucous glands.
2. glands that have both exocrine and endocrine portions.
Moll's g's ciliary glands.
Montgomery's g's sebaceous glands in the mammary areola; called also areolar glands.
mucous g's glands that secrete mucus.
olfactory g's small mucous glands in the olfactory mucosa; called also Bowman's glands.
parathyroid g's see parathyroid glands.
parotid g's see parotid glands.
peptic g's gastric glands that secrete pepsin.
pineal gland pineal body.
pituitary gland see pituitary gland.
preputial g's small sebaceous glands of the corona of the penis and the inner surface of the prepuce, which secrete smegma; called also Littre's glands and Tyson's glands.
prostate gland prostate.
pyloric g's the mucin-secreting glands of the pyloric part of the stomach.
salivary g's see salivary glands.
sebaceous gland a type of holocrine gland of the corium that secretes an oily material (sebum) into the hair follicles.

Glands: The relationship of the hair follicle, eccrine and apocrine sweat glands and sebaceous glands. From Copstead, 1995.
sentinel gland an enlarged lymph node, considered to be pathognomonic of some pathologic condition elsewhere.
seromucous g's glands that are both serous and mucous.
serous gland a gland that secretes a watery albuminous material, commonly but not always containing enzymes.
sex gland (sexual gland) gonad.
simple gland one with a nonbranching duct.
Skene's g's the largest of the female urethral glands, which open into the urethral orifice; they are regarded as homologous with the prostate. Called also paraurethral ducts.
solitary g's solitary follicles.
sublingual gland a salivary gland on either side under the tongue.
submandibular gland (submaxillary gland) a salivary gland on the inner side of each ramus of the mandible.
sudoriferous gland (sudoriparous gland) sweat gland.
suprarenal gland adrenal gland.
sweat gland see sweat gland.
target gland any gland affected by a secretion or other stimulus from another gland, such as those affected by the secretions of the pituitary gland.
tarsal g's meibomian glands.
thymus gland thymus.
thyroid gland see thyroid gland.
tubular gland any gland made up of or containing a tubule or tubules.
Tyson's g's preputial glands.
unicellular gland a single cell that functions as a gland, e.g., a goblet cell.
urethral g's mucous glands in the wall of the urethra; in the male, called also Littre's glands.
uterine g's simple tubular glands found throughout the thickness and extent of the endometrium; they become enlarged during the premenstrual period.
vesical g's mucous glands sometimes found in the wall of the urinary bladder, especially in the area of the trigone.
vulvovaginal g's Bartholin's glands.
Waldeyer's g's glands in the attached edge of the eyelid.
Weber's g's the tubular mucous glands of the tongue.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
gland
(gland), [TA]An organized aggregation of cells functioning as a secretory or excretory organ.
Synonym(s): glandula (1) [TA]
[L. glans, acorn]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
gland
(glănd)n.
1.
a. Any of various organs or cell groups, such as the adrenal glands and the salivary glands, that are of endothelial origin and secrete a substance that is used or excreted by the body.
b. Any of various organs, such as lymph nodes, that resemble true glands but perform a nonsecretory function.
2. Botany An organ or a structure that secretes a substance.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
gland
(gland) [TA]An organized aggregation of cells functioning as a secretory or excretory organ.
Synonym(s): glandula (1) .
Synonym(s): glandula (1) .
[L. glans, acorn]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
gland
A cell or organized collection of cells capable of abstracting substances from the blood, synthesizing new substances, and secreting or excreting them into the blood (endocrine glands), into other bodily structures or on to surfaces, including the skin (exocrine glands). The simplest glands are single mucus-secreting goblet cells. Glands also produce digestive enzymes, hormones, tears, sweat, milk and sebum. LYMPH NODES are often miscalled ‘glands’.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
gland
an organ producing substances which are then secreted to the outside of the gland, sometimes by means of a duct, as in the exocrine glands, for example, the salivary mammary, lachrymal glands, but also in the case of ENDOCRINE GLANDS directly into the blood or lymphatic systems. Occasionally individual cells act as glands, for example, gland cells of Hydra producing digestive enzymes.Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
Gland
A collection of cells whose function is to release certain chemicals, or hormones, which are important to the functioning of other, sometimes distantly located, organs or body systems.
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
gland
An aggregation of cells which secretes or excretes a substance. There are two main groups of glands: (1) The endocrine glands which have no duct and whose secretion (a hormone) is absorbed directly into the blood. Examples: adrenal gland, pineal gland, pituitary gland, thyroid gland. (2) The exocrine glands whose secretion reaches the surface by means of ducts. There are three main types of secretion by exocrine glands: the serous glands which secrete a watery substance rich in proteins (e.g. lacrimal gland, sweat glands), the mucous glands which secrete mucus, a viscous product (e.g. goblet cells), and the sebaceous glands which secrete a lipid substance (e.g. meibomian glands).
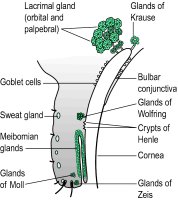
accessory lacrimal gland's They are the glands of Krause and Wolfring. These glands are histologically identical to the main lacrimal gland, but are located within the eyelids. These glands are responsible for basal (not reflex) tear secretion and appear to be under sympathetic neural control.
gland's of Ciaccio See glands of Wolfring.
ciliary sebaceous gland's See glands of Zeis.
ciliary sweat gland's See glands of Moll.
conjunctival gland Any gland that secretes a substance into the conjunctiva, such as the lacrimal, meibomian, Krause and Wolfring glands or a goblet cell.
gland's of Henle These are not really glands. They are folds in the mucous membrane of the palpebral conjunctiva, situated between the tarsal plates and the fornices, in which there are goblet cells (Fig. G2). Syn. crypts of Henle (strictly speaking this term refers only to the pit-like depressions).
gland's of Krause Accessory lacrimal glands of the conjunctiva having the same structure as the main lacrimal gland. They are located in the subconjunctival connective tissue of the fornix, especially the superior fornix (Fig. G2).
lacrimal gland A compound gland situated above and to the outer side of the globe of the eye. It consists of two portions: (1) a large orbital or superior portion; and (2) a small palpebral or inferior portion. It secretes the middle aqueous layer of the tears through about a dozen fine ducts into the conjunctival sac at the upper fornix although one or two may also open into the outer part of the lower fornix (Fig. G2). See dacryoadenitis; dacryops; fossa for the lacrimal gland; zygomatic nerve; tear duct.
gland's of Manz Tiny glands located near the limbus. They secrete mucin. The existence of these glands in man is not established.
meibomian gland's Sebaceous glands located in the tarsal plates of the eyelids whose ducts empty into the eyelid margin. They are arranged parallel with each other, perpendicular to the lid margin, about 25 for the upper lid and 20 for the lower. They secrete sebum. This sebaceous material provides the outermost oily (or lipid) layer of the precorneal tear film. It prevents the lacrimal fluid from overflowing onto the outer surface of the eyelid. It also makes for an airtight closure of the lids and prevents the tears from macerating the skin. The meibomian glands can be seen showing through the conjunctiva of fair-skinned people as yellow streaks (Fig. G2). Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) may be induced by blepharitis, chalazion, contact lens wear (particularly soft lenses) and ageing. The most common sign is a cloudy or absent secretion upon expression with symptoms of a mild dry eye. Hot compresses and lid massage will cure more than half of the patients; oral tetracycline will help in many of the others. Syn. palpebral follicles; tarsal glands. See posterior blepharitis; chalazion; precorneal film; internal hordeolum; keratoconjunctivitis sicca; meibomianitis; tarsus; Tearscope plus.
gland's of Moll Sweat glands of the eyelids. They are situated in the region of the eyelashes (Fig. G2). Syn. ciliary sweat glands.
tarsal gland's See meibomian glands.
gland's of Wolfring Accessory lacrimal glands of the upper eyelid situated in the region of the upper border of the tarsus (Fig. G2). Syn. glands of Ciaccio.
gland's of Zeis Sebaceous glands of the eyelids which are attached directly to the follicles of the eyelashes. Their secretion contributes to the oily layer of the precorneal film (Fig. G2). Syn. ciliary sebaceous glands. See marginal blepharitis; hordeolum.
accessory lacrimal gland's They are the glands of Krause and Wolfring. These glands are histologically identical to the main lacrimal gland, but are located within the eyelids. These glands are responsible for basal (not reflex) tear secretion and appear to be under sympathetic neural control.
gland's of Ciaccio See glands of Wolfring.
ciliary sebaceous gland's See glands of Zeis.
ciliary sweat gland's See glands of Moll.
conjunctival gland Any gland that secretes a substance into the conjunctiva, such as the lacrimal, meibomian, Krause and Wolfring glands or a goblet cell.
gland's of Henle These are not really glands. They are folds in the mucous membrane of the palpebral conjunctiva, situated between the tarsal plates and the fornices, in which there are goblet cells (Fig. G2). Syn. crypts of Henle (strictly speaking this term refers only to the pit-like depressions).
gland's of Krause Accessory lacrimal glands of the conjunctiva having the same structure as the main lacrimal gland. They are located in the subconjunctival connective tissue of the fornix, especially the superior fornix (Fig. G2).
lacrimal gland A compound gland situated above and to the outer side of the globe of the eye. It consists of two portions: (1) a large orbital or superior portion; and (2) a small palpebral or inferior portion. It secretes the middle aqueous layer of the tears through about a dozen fine ducts into the conjunctival sac at the upper fornix although one or two may also open into the outer part of the lower fornix (Fig. G2). See dacryoadenitis; dacryops; fossa for the lacrimal gland; zygomatic nerve; tear duct.
gland's of Manz Tiny glands located near the limbus. They secrete mucin. The existence of these glands in man is not established.
meibomian gland's Sebaceous glands located in the tarsal plates of the eyelids whose ducts empty into the eyelid margin. They are arranged parallel with each other, perpendicular to the lid margin, about 25 for the upper lid and 20 for the lower. They secrete sebum. This sebaceous material provides the outermost oily (or lipid) layer of the precorneal tear film. It prevents the lacrimal fluid from overflowing onto the outer surface of the eyelid. It also makes for an airtight closure of the lids and prevents the tears from macerating the skin. The meibomian glands can be seen showing through the conjunctiva of fair-skinned people as yellow streaks (Fig. G2). Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) may be induced by blepharitis, chalazion, contact lens wear (particularly soft lenses) and ageing. The most common sign is a cloudy or absent secretion upon expression with symptoms of a mild dry eye. Hot compresses and lid massage will cure more than half of the patients; oral tetracycline will help in many of the others. Syn. palpebral follicles; tarsal glands. See posterior blepharitis; chalazion; precorneal film; internal hordeolum; keratoconjunctivitis sicca; meibomianitis; tarsus; Tearscope plus.
gland's of Moll Sweat glands of the eyelids. They are situated in the region of the eyelashes (Fig. G2). Syn. ciliary sweat glands.
tarsal gland's See meibomian glands.
gland's of Wolfring Accessory lacrimal glands of the upper eyelid situated in the region of the upper border of the tarsus (Fig. G2). Syn. glands of Ciaccio.
gland's of Zeis Sebaceous glands of the eyelids which are attached directly to the follicles of the eyelashes. Their secretion contributes to the oily layer of the precorneal film (Fig. G2). Syn. ciliary sebaceous glands. See marginal blepharitis; hordeolum.
Millodot: Dictionary of Optometry and Visual Science, 7th edition. © 2009 Butterworth-Heinemann
gland
(gland) [TA]Organized aggregation of cells functioning as a secretory or excretory organ.
[L. glans, acorn]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about gland
Q. Anyone know if there is a connection between Fibromyalgia and your Thyroid gland? I have Fibromyalgia and I read that if your diagnosed with this you can have Thyroid problems also. If anyone knows out there please inform me. Many thanks.
A. Below is an interesting article on the subject. A significant percentage of the estimated 20 million people with hypothyroidism end up also being diagnosed with fibromyalgia. Some experts believe that like most cases of hypothyroidism, fibromyalgia is also autoimmune in nature. Others believe that fibromyalgia may be one manifestation of an under active metabolism – hypometabolism – and is therefore one variation on thyroid dysfunction.
http://thyroid.about.com/cs/fibromyalgiacfs/a/fibrothyroid.htm
http://thyroid.about.com/cs/fibromyalgiacfs/a/fibrothyroid.htm
Q. my friend ate a bar of chocolate and now her left neck gland is swollen any ideas why? no other symptoms
A. it can be an infection -just like brandon said- or although this is rare, it can also be an allergic reaction.
if it is an infection, you can usually find such other infection symptoms like : fever, pain in that swollen area, increased white blood cells (in blood work test), etc.
if it is an allergy, usually it will fade away itself in couple of days, or you can just try to consume anti-allergic drugs, such as : loratadine and maybe combined with dexamethasone.
Good luck, and stay healthy always..
More discussions about glandif it is an infection, you can usually find such other infection symptoms like : fever, pain in that swollen area, increased white blood cells (in blood work test), etc.
if it is an allergy, usually it will fade away itself in couple of days, or you can just try to consume anti-allergic drugs, such as : loratadine and maybe combined with dexamethasone.
Good luck, and stay healthy always..
This content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.