occlusion
[ŏ-kloo´zhun]1. obstruction.
2. the trapping of a liquid or gas within cavities in a solid or on its surface.
3. the relation of the teeth of both jaws when in functional contact during activity of the mandible.
4. momentary complete closure of some area in the vocal tract, causing breathing to stop and pressure to accumulate.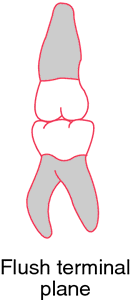

Normal occlusion of the primary molars. From Darby and Walsh, 1994.
abnormal occlusion malocclusion.
central occlusion (centric occlusion) occlusion of the teeth when the mandible is in centric relation to the maxilla, with full occlusal surface contact of the upper and lower teeth in habitual occlusion.
coronary occlusion see coronary occlusion.
eccentric occlusion occlusion of the teeth when the lower jaw has moved from the centric position.
functional occlusion contact of the maxillary and mandibular teeth that provides the highest efficiency in the centric position and during all exclusive movements of the jaw that are essential to mastication without producing trauma.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
cen·tric oc·clu·sion
1. the relation of opposing occlusal surfaces that provides the maximum planned contact and/or intercuspation;
2. the occlusion of the teeth when the mandible is in centric relation to the maxillae.
Synonym(s): centric contact
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
cen·tric oc·clu·sion
(sen'trik ŏ-klū'zhŭn)1. The relation of opposing occlusal surfaces that provides the maximum contact and intercuspation.
2. The occlusion of the teeth when the mandible is in centric relation to the maxillae.
Synonym(s): acquired centric, habitual centric, intercuspal position.
Synonym(s): acquired centric, habitual centric, intercuspal position.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
cen·tric oc·clu·sion
(sen'trik ŏ-klū'zhŭn)1. Relation of opposing occlusal surfaces that provides maximal planned contact and/or intercuspation.
2. Occlusion of the teeth when mandible is in centric relation to the maxillae.
Synonym(s): acquired centric, centric contact, habitual centric.
Synonym(s): acquired centric, centric contact, habitual centric.
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012