canal
[kah-nal´]a relatively narrow tubular passage or channel.
adductor canal Hunter's canal.
Alcock's canal a tunnel formed by a splitting of the obturator fascia, which encloses the pudendal vessels and nerve.
alimentary canal see alimentary canal.
anal canal the terminal portion of the alimentary canal, from the rectum to the anus.
atrioventricular canal the common canal connecting the primordial atrium and ventricle; it sometimes persists as a congenital anomaly.
birth canal the canal through which the fetus passes in birth.
carotid canal one in the pars petrosa of the temporal bone, transmitting the internal carotid artery to the cranial cavity.
cervical canal the part of the uterine cavity lying within the cervix.
condylar canal an occasional opening in the condylar fossa for transmission of the transverse sinus; called also posterior condyloid foramen.
canal of Corti a space between the outer and inner rods of Corti.
femoral canal the cone-shaped medial part of the femoral sheath lateral to the base of Gimbernat's ligament.
haversian canal any of the anastomosing channels of the haversian system in compact bone, containing blood and lymph vessels, and nerves.
Hunter's canal a fascial tunnel in the middle third of the medial part of the thigh, containing the femoral vessels and saphenous nerve. Called also adductor canal.
hypoglossal canal an opening in the occipital bone, transmitting the hypoglossal nerve and a branch of the posterior meningeal artery; called also anterior condyloid foramen.
infraorbital canal a small canal running obliquely through the floor of the orbit, transmitting the infraorbital vessels and nerve.
inguinal canal the oblique passage in the lower anterior abdominal wall on either side, through which passes the round ligament of the uterus in the female, and the spermatic cord in the male.
medullary canal
1. spinal canal.
2. marrow cavity.
optic canal a passage for the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery at the apex of the orbit; called also optic foramen.
pulp canal root canal.
root canal that part of the pulp cavity extending from the pulp chamber to the apical foramen. Called also pulp canal.
sacral canal the continuation of the spinal canal through the sacrum.
Schlemm's canal venous sinus of sclera.
semicircular c's see semicircular canals.
spinal canal (vertebral canal) the canal formed by the series of vertebral foramina together, enclosing the spinal cord and meninges.
Volkmann's c's canals communicating with the haversian canals, for passage of blood vessels through bone.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
ca·nal
(kă-nal'), [TA] Synonym(s): canalis [TA]
[L. canalis]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
canal
(kə-năl′)n.
Anatomy A tube, duct, or passageway.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
canal
AnatomyA furrow or conduit.
Vox populi
A narrow, usually manmade body of water which provides a route of maritime transportation.
Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
ca·nal
(kă-nal') [TA]A duct or channel; a tubular structure.
Synonym(s): canalis [TA] .
Synonym(s): canalis [TA] .
[L. canalis]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
canal
A tubular channel which allows the passage of air, food, blood, excretions, secretions, or anatomical structures such as nerves or blood vessels.
Cloquet's canal See hyaloid canal.
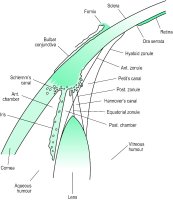
Hannover's canal A space about the equator of the crystalline lens made up between the anterior and posterior parts of the zonule of Zinn and containing aqueous humour and zonular fibres (Fig. C1).
hyaloid canal A channel in the vitreous humour, running from the optic disc to the crystalline lens. In fetal life this canal contains the hyaloid artery, which nourishes the lens, but it usually disappears prior to birth. Syn. central canal; Cloquet's canal; Stilling's canal. See hyaloid remnant.
infraorbital canal A channel beginning at the infraorbital groove in the floor of the orbit and ending at the infraorbital foramen of the maxillary bone opening onto the face below the inferior orbital margin. It is a channel for the infraorbital artery and the infraorbital nerve.
nasolacrimal canal See Table O4.
optic canal A canal leading from the middle cranial fossa to the apex of the orbit in the small wing of the sphenoid bone through which pass the optic nerve and the ophthalmic artery. Syn. optic foramen. See Table O4.
canal of Petit A space between the posterior fibres of the zonule of Zinn and the anterior surface of the vitreous humour (Fig. C1).
Schlemm's canal A circular venous sinus located in the corneoscleral junction, anterior to the scleral spur and receiving aqueous humour from the anterior chamber and discharging into the aqueous and the anterior ciliary veins (Fig. C1). Syn. scleral sinus; sinus circularis iridis; sinus venosus sclerae; venous circle of Leber. See trabecular meshwork; scleral spur; aqueous vein.
Stilling's canal See hyaloid canal.
Cloquet's canal See hyaloid canal.
Hannover's canal A space about the equator of the crystalline lens made up between the anterior and posterior parts of the zonule of Zinn and containing aqueous humour and zonular fibres (Fig. C1).
hyaloid canal A channel in the vitreous humour, running from the optic disc to the crystalline lens. In fetal life this canal contains the hyaloid artery, which nourishes the lens, but it usually disappears prior to birth. Syn. central canal; Cloquet's canal; Stilling's canal. See hyaloid remnant.
infraorbital canal A channel beginning at the infraorbital groove in the floor of the orbit and ending at the infraorbital foramen of the maxillary bone opening onto the face below the inferior orbital margin. It is a channel for the infraorbital artery and the infraorbital nerve.
nasolacrimal canal See Table O4.
optic canal A canal leading from the middle cranial fossa to the apex of the orbit in the small wing of the sphenoid bone through which pass the optic nerve and the ophthalmic artery. Syn. optic foramen. See Table O4.
canal of Petit A space between the posterior fibres of the zonule of Zinn and the anterior surface of the vitreous humour (Fig. C1).
Schlemm's canal A circular venous sinus located in the corneoscleral junction, anterior to the scleral spur and receiving aqueous humour from the anterior chamber and discharging into the aqueous and the anterior ciliary veins (Fig. C1). Syn. scleral sinus; sinus circularis iridis; sinus venosus sclerae; venous circle of Leber. See trabecular meshwork; scleral spur; aqueous vein.
Stilling's canal See hyaloid canal.
Millodot: Dictionary of Optometry and Visual Science, 7th edition. © 2009 Butterworth-Heinemann
ca·nal
(kă-nal') [TA][L. canalis]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about canal
Q. How much does a root canal hurt? I have to get a root canal for my bottom tooth. I was wondering how much they hurt. And do you have any suggestions that help distract from the pain? Thanks.
A. i did one about two years ago- even the injection wasn't too bad! didn't feel a thing. but after the anesthesia worn off it hurt. but then the dentist told me to take Advil or any other NSAID and it helped.
More discussions about canalThis content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.