auricle
[aw´rĭ-k'l]1. the projecting part of the ear lying outside the head; called also pinna. 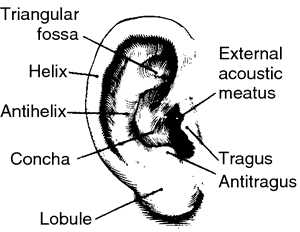

Auricle.
2. the ear-shaped appendage of either atrium of the heart; formerly used to designate the entire atrium.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
au·ri·cle
(aw'ri-kl), [TA] Avoid the outmoded use of this word in the sense of atrium.The projecting shell-like structure on the side of the head, constituting, with the external acoustic meatus, the external ear. Synonym(s): auricula (1) [TA], pinna1 ☆ , ala auris
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
auricle
(ôr′ĭ-kəl)n.
1. Anatomy
a. The outer projecting portion of the ear. Also called pinna.
b. See atrium.
2. Biology An earlobe-shaped part, process, or appendage, especially at the base of an organ.
au′ri·cled (-kəld) adj.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
auricle
(1) (Right or left) atrial auricula, auricula atrii dextri/sinistri—a conical scrotiform structure that projects from either the right or left atrium.(2) Pinna of the ear, auricula auris externa—the fan-shaped fibrocartilaginous plate located around the ear canal on each side of the head, which is the more prominent portion of the external ear, the lesser and lower portion being the earlobe.
Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
au·ri·cle
(awr'i-kĕl) [TA]1. The projecting shell-like structure on the side of the head, constituting, with the external acoustic meatus, the external ear.
Synonym(s): auricula (1) , pinna (1) .
Synonym(s): auricula (1) , pinna (1) .
2. Synonym(s): auricle of atrium.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
auricle
1. The pinna, or external ear.
2. An obsolescent term for one of the upper chambers of the heart (atrium).
Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
auricle
- a former term for the ATRIUM of the heart.
- an alternative term for the PINNA (outer ear).
- (also called auricula) an ear-shaped part or appendage, such as that occurring at the base of some leaves.
Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
Auricle
The external structure of the ear.
Mentioned in: Otitis Externa
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
au·ri·cle
(awr'i-kĕl) [TA] Avoid the outmoded use of this word in the sense of atrium.The projecting shell-like structure on the side of the head, constituting, with the external acoustic meatus, the external ear.
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012