vertebra
[ver´tĕ-brah] (L.)any of the separate segments comprising the spine (vertebral column). The vertebrae support the body and provide the protective bony corridor (the spinal or vertebral canal) through which the spinal cord passes. The 33 bones that make up the spine differ considerably in size and structure according to location. There are seven cervical (neck) vertebrae, 12 thoracic (high back), five lumbar (low back), five sacral (near the base of the spine), and four coccygeal (at the base). The five sacral vertebrae are fused to form the sacrum, and the four coccygeal vertebrae are fused to form the coccyx.
The weight-bearing portion of a typical vertebra is the vertebral body, the most forward portion. This is a cylindrical structure that is separated from the vertebral bodies above and below by disks of cartilage and fibrous tissue. These intervertebral disks act as cushions to absorb the mechanical shock of walking, running, and other activity. Sometimes rupture or herniation of a disk may occur (see herniated disk).
A semicircular arch of bone (the vertebral arch) protrudes from the back of each vertebral body, surrounding the spinal cord. Directly in its midline a bony projection, the spinous process, grows backward from the arch. The spinous process can be felt on the back as a hard knob. Three pairs of outgrowths project from the arch. One of these protrudes horizontally on each side and in the thorax connects with the ribs. The remaining two form joints with the vertebrae above and below. The joints permit the spine to bend flexibly. The vertebrae are held firmly in place by a series of strong ligaments.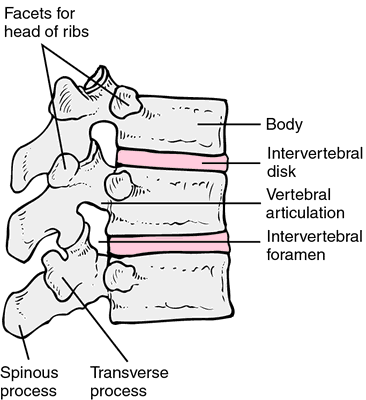
The weight-bearing portion of a typical vertebra is the vertebral body, the most forward portion. This is a cylindrical structure that is separated from the vertebral bodies above and below by disks of cartilage and fibrous tissue. These intervertebral disks act as cushions to absorb the mechanical shock of walking, running, and other activity. Sometimes rupture or herniation of a disk may occur (see herniated disk).
A semicircular arch of bone (the vertebral arch) protrudes from the back of each vertebral body, surrounding the spinal cord. Directly in its midline a bony projection, the spinous process, grows backward from the arch. The spinous process can be felt on the back as a hard knob. Three pairs of outgrowths project from the arch. One of these protrudes horizontally on each side and in the thorax connects with the ribs. The remaining two form joints with the vertebrae above and below. The joints permit the spine to bend flexibly. The vertebrae are held firmly in place by a series of strong ligaments.

Structure of vertebrae.
cervical vertebrae the upper seven vertebrae, constituting the skeleton of the neck.
coccygeal vertebrae the lowest segments of the vertebral column, comprising three to five rudimentary vertebrae that form the coccyx.
cranial vertebra the segments of the skull and facial bones, regarded by some as modified vertebrae.
vertebra denta´ta the second cervical vertebra, or axis.
dorsal vertebrae thoracic vertebrae.
false vertebrae those vertebrae that normally fuse with adjoining segments: the sacral and coccygeal vertebrae.
lumbar vertebrae the five vertebrae between the thoracic vertebrae and the sacrum.
vertebra mag´na the sacrum.
odontoid vertebra the second cervical vertebra, or axis.
vertebra pla´na a condition of spondylitis in which the body of the vertebra is reduced to a sclerotic disk.
sacral vertebrae the vertebrae just below the lumbar vertebrae, usually five in number and fused to form the sacrum.
thoracic vertebrae the twelve vertebrae between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae, giving attachment to the ribs and forming part of the posterior wall of the thorax.
true vertebrae those segments of the vertebral column that normally remain unfused throughout life: the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
Thoracic vertebrae
The vertebrae in the chest region to which the ribs attach.
Mentioned in: Spinal Instrumentation
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.