electrocardiogram
(ECG, EKG) [e-lek″tro-kahr´de-o-gram″]the record produced by electrocardiography; a tracing representing the heart's electrical action derived by amplification of the minutely small electrical impulses normally generated by the heart.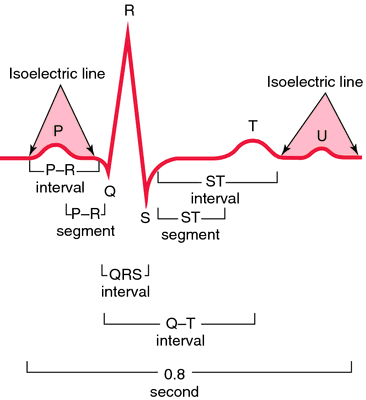

Normal electrocardiogram. Heart action during P-R interval: (1) Atrial contraction begins at peak of P wave. (2) P-R interval—atrial contraction. (3) Ventricles relaxed. Heart action during QRS complex: (1) Ventricular contraction begins at peak of R. (2) A-V (mitral and tricuspid) valves close, causing S1 sound. (3) Ventricles contract. (4) Atrial relaxation begins. Heart action during S-T segment: (1) Semilunar valves open (aortic and pulmonic). (2) Ejection of blood from ventricles–systole. Heart action during T wave: (1) Slowing of ejection from ventricles. (2) Closure of semilunar valves (aortic and pulmonic) causing S2 sound. Heart action during T-P interval: (1) Relaxation of ventricles. (2) A-V valves open. (3) Filling of ventricles, causing S3 sound.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
ECG
Abbreviation for electrocardiogram.
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
ECG
(ē′sē′jē′)n. Chiefly British
1. An electrocardiogram.
2. An electrocardiograph.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
ECG
Abbreviation for:echocardiography
electrocardiogram
electrocardiography
equine chorionic gonadotropin
Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
ECG
1. Electrocardiogram, see there, EKG.
2. Echocardiogram, see there.
McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
ECG
Abbreviation for electrocardiogram.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
ECG
Abbrev. for ELECTROCARDIOGRAM.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005

Fig. 140 ECG . A tracing of the electric currents that initiate the heartbeat. The broken line indicates diastole, the solid line systole.
ECG (electrocardiogram)
a recording of the electrical changes occurring as the heart beats (see HEART, CARDIAC CYCLE that can be used in the diagnosis of heart malfunction. Each cardiac cycle produces three distinct ECG waves, designated as P, QRS and T. These waves represent changes in electrical potential between two regions on the surface of the heart. The spread of atrial depolarization creates the P wave; spread of ventricular depolarization is represented by the QRS wave; repolarization of the ventricles produces the T wave. To obtain an ECG, electrodes are attached to various parts of the body surface, usually both arms and the left leg.Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
ECG or EKG
A record of the waves that relates to the electrical impulses produced at each beat of the heart.
Mentioned in: Aortic Valve Stenosis, Electrocardiography
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.