aorta
[a-or´tah] (pl. aor´tae, aortas) (L.) the great artery arising from the left ventricle, being the main trunk from which the systemic arterial system proceeds. It has four divisions: the ascending aorta, the aortic arch, the thoracic aorta, and the abdominal aorta. See Appendix of Arteries and see
circulatory system.
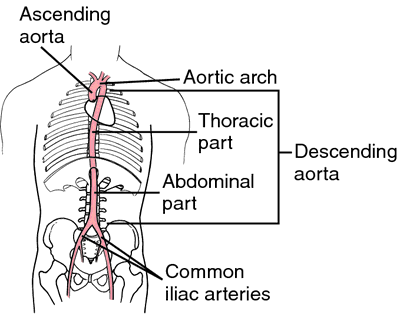
Aorta, arising from the left ventricle, ascending, arching, then descending through the thorax to the abdomen, where it divides into the common iliac arteries. From Dorland's, 2000.
overriding aorta a congenital anomaly occurring in
tetralogy of Fallot, in which the aorta is displaced to the right so that it appears to arise from both ventricles and straddles the ventricular septal defect.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
a·or·ta
, gen. and pl. a·or·tae
(ā-ōr'tă, ā-ōr'tē), [TA] A large artery of the elastic type that is the main trunk of the systemic arterial system, arising from the base of the left ventricle and ending at the left side of the body of the fourth lumbar vertebra by dividing to form the right and left common iliac arteries. The aorta is subdivided into: ascending aorta; aortic arch; and descending aorta, which is in turn, divided into the thoracic aorta and the abdominal aorta.
[Mod. L. fr. G. aortē, from aeirō, to lift up]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
aorta
(ā-ôr′tə)n. pl. aor·tas or
aor·tae (-tē) The main trunk of the systemic arteries, carrying blood from the left side of the heart to the arteries of all limbs and organs except the lungs.
a·or′tal, a·or′tic adj.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
a·or·ta
, pl. aortae (ā-ōr'tă, -tē) [TA] A large artery that is the main trunk of the systemic arterial system, arising from the left ventricle and ending at the left side of the body of the fourth lumbar vertebra by dividing to form the right and left common iliac arteries. The aorta is made up of the ascending aorta, aortic arch, and descending aorta, which is divided into the thoracic aorta and the abdominal aorta.
[Mod. L. fr. G. aortē, from aeirō, to lift up]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
aorta
The main, and largest ARTERY of the body which springs directly from the lower pumping chamber on the left side of the heart and gives off branches to the heart muscle, the head, arms, trunk, chest and abdominal organs and legs.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
aorta
the ‘great artery’ of the mammalian BLOOD CIRCULATORY SYSTEM. It carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle of the heart around the AORTIC ARCH and along the dorsal aorta which runs the length of the trunk, giving rise to several branches to individual body organs. The ventral aorta is the main artery in fish and lower chordates which carries blood from the heart to the gills.Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
Aorta
The main blood vessel that leads away from the heart and the body's largest artery. The aorta carries blood from the heart through the chest and abdomen, providing major branches to all of the organs in the body.
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
a·or·ta
, pl. aortae (ā-ōr'tă, -tē) [TA] Large elastic artery that is the main trunk of the systemic arterial system, arising from base of left ventricle and ending at left side of body of fourth lumbar vertebra by dividing to form right and left common iliac arteries.
[Mod. L. fr. G. aortē, from aeirō, to lift up]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
Patient discussion about Aorta
Q. Why does Aortic stenosis causes an enlarged heart? My father was recently diagnosed as suffering from enlarged heart due to his Aortic stenosis. what is the connection between those to conditions? As far as I understand that aortic stenosis mean that the aortic valve is too small not too large...
A. there are several explanations for the enlargement of the heart that occurs due to Aortic stenosis. the most reasonable is that the mechanical power that the heart uses makes it bigger. it easy to see it here: http://www.marvistavet.com/assets/images/aortic_stenosis.gif
this is called Left Ventricular Hypertrophy or LVH in abbreviations.
this is a classic LVH E.C.G.
http://www.frca.co.uk/images_main/resources/ECG/ECGresource39.jpg
Q. How does alcohol affect someone who has been diagnosed with aortic valve stenosis? My brother has been diagnosed with aortic valve stenosis and also is a smoker and does drink alcohol on the weekends. He knows that he should stop smoking but what about the effects of alcohol? Does this also contribute to his stenosis?
A. Alcohol changes blood pressure and speed of the heart- that is not a good idea if you have an Aortic stenosis. Could probably makes things worst. I would avoid alcohol… but he should ask GP.
Q. Is there a good screening test for aortic abdominal aneurysm? A friend of mine was diagnosed with an aortic abdominal aneurysm. I am afraid i might have this condition too. is there any screening test that is good for me?
A. Today there are "mobile" testing centers that charge to use ultrasound technology to detect such things as AAA. I would highly recommend it only because it can act as a preventative measure. I am 50 years old and just suffered a ruptured AAA that very nearly killed me. I was the fortunate one. This very possibly could have detected it before it actually ruptured. You may want to check in your local areas for these mobile testing centers.
More discussions about AortaThis content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.
