magnesium
(Mg) [mag-ne´ze-um]a chemical element, atomic number 12, atomic weight 24.312. (See Appendix 6.) Its salts are essential in nutrition, being required for the activity of many enzymes, especially those concerned with oxidative phosphorylation. It is found in the intra- and extracellular fluids and is excreted in urine and feces. The normal serum level is approximately 2 mEq/L. Magnesium deficiency causes irritability of the nervous system with tetany, vasodilation, convulsions, tremors, depression, and psychotic behavior.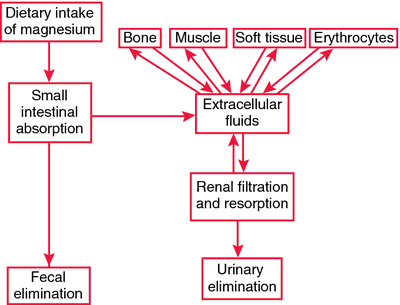

Homeostasis of magnesium in extracellular fluids. The normal serum magnesium level is regulated by intestinal and renal function. Most of the body's magnesium is stored in bones, muscle, and soft tissue. From Malarkey and McMorrow, 2000.
magnesium carbonate an antacid.
magnesium chloride an electrolyte replenisher and a pharmaceutic necessity for hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis fluids.
magnesium citrate a saline laxative used for bowel evacuation before diagnostic procedures or surgery of the colon; administered orally.
magnesium salicylate see salicylate.
magnesium silicate MgSiO3, a silicate salt of magnesium; the most common hydrated forms found in nature are asbestos and talc.
magnesium sulfate Epsom salt; an anticonvulsant and electrolyte replenisher, also used as a laxative and local antiinflammatory.
magnesium trisilicate a combination of magnesium oxide and silicon dioxide with varying proportions of water; used as a gastric antacid.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
mag·ne·si·um sa·lic·y·late
a sodium-free salicylate derivative with antiinflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic actions; used for relief of mild to moderate pain.
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012