ampicillin sodium
Pharmacologic class: Aminopenicillin
Therapeutic class: Anti-infective
Pregnancy risk category B
Action
Destroys bacteria by inhibiting bacterial cell-wall synthesis during microbial multiplication
Availability
Capsules: 250 mg, 500 mg
Oral suspension: 125 mg/5 ml, 250 mg/5 ml
Powder for injection: 125 mg, 250 mg, 500 mg, 1 g, 2 g, 10 g
Indications and dosages
➣ Respiratory tract, skin, and soft-tissue infections caused by Haemophilus influenzae, staphylococci, and streptococci
Adults and children weighing 40 kg (88 lb) or more: 250 to 500 mg I.V. or I.M. q 6 hours
Adults and children weighing less than 40 kg (88 lb): 25 to 50 mg/kg/day I.M. or I.V. in divided doses q 6 to 8 hours
Adults and children weighing more than 20 kg (44 lb): 250 mg P.O. q 6 hours
Children weighing 20 kg (44 lb) or less: 50 mg/kg/day P.O. in divided doses q 6 to 8 hours
➣ Bacterial meningitis caused by Neisseria meningitidis, Escherichia coli, group B streptococci, or Listeria monocytogenes; septicemia caused by Streptococcus species, penicillin G-susceptible staphylococci, enterococci, E. coli, Proteus mirabilis, or Salmonella species
Adults: 150 to 200 mg/kg/day by continuous I.V. infusion or I.M. injection in equally divided doses q 3 to 4 hours, to a maximum dosage of 14 g
Children: 100 to 200 mg/kg/day I.V. in divided doses q 3 to 4 hours
➣ GI or urinary tract infections, including Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection in women
Adults and children weighing more than 40 kg (88 lb): 500 mg I.M. or I.V. q 6 hours
Adults and children weighing 40 kg (88 lb) or less: 50 to 100 mg/kg/day I.M. or I.V. in equally divided doses q 6 to 8 hours
➣ Endocarditis prophylaxis for dental, oral, or upper respiratory tract procedures
Adults: 2 g I.M. or I.V. within 30 minutes before procedure
Children: 50 mg/kg I.V. or I.M. within 30 minutes before procedure
➣ Prevention of bacterial endocarditis before GI or GU surgery or instrumentation
High-risk adults: 2 g I.M. or I.V. with gentamicin 1.5 mg/kg I.M. or I.V. within 30 minutes before procedure. Six hours later, give ampicillin 1 g I.M. or I.V., or amoxicillin 1 g P.O.
High-risk children: 50 mg/kg I.M. or I.V. with 1.5 mg/kg of gentamicin I.M. or I.V. within 30 minutes before procedure; 6 hours later, give ampicillin 25 mg/kg I.M. or I.V. or ampicillin 25 mg/kg P.O.
Moderate-risk adults: 2 g I.M. or I.V. within 30 minutes before procedure Moderate-risk children: 50 mg/kg I.M. or I.V. within 30 minutes before procedure
➣ Prophylaxis for neonatal group B streptococcal disease
Adult women: During labor, loading dose of 2 g I.V.; then 1 g I.V. q 4 hours until delivery
➣ N. gonorrhoeae infections
Adults: Single dose of 3.5 g P.O. given with l g probenecid
Children weighing 40 kg (88 lb) or more: 500 mg I.M. or I.V. q 6 hours
Children weighing less than 40 kg (88 lb): 50 mg/kg/day in divided doses q 6 to 8 hours
➣ Urethritis caused by N. gonorrhoeae (in males)
Adults and children weighing 40 kg (88 lb) or more: 500 mg I.V. or I.M., repeated 8 to 12 hours later
➣ Prophylaxis against sexually transmitted diseases in adult rape victims
Adults: 3.5 g P.O. with l g probenecid as a single dose
Dosage adjustment
• Renal impairment
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to penicillins, cephalosporins, imipenem, or other beta-lactamase inhibitors
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• severe renal insufficiency, infectious mononucleosis
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients.
Administration
• Ask patient about history of penicillin allergy before giving.
• For I.V. use, mix powder with bacteriostatic water for injection in amount listed on label.
• For direct I.V. injection, give over 10 to 15 minutes. Don't exceed 100 mg/minute.
• For intermittent I.V. infusion, mix with 50 to 100 ml of normal saline solution and give over 15 to 30 minutes.
• Change I.V. site every 48 hours.
• Give oral doses 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals.
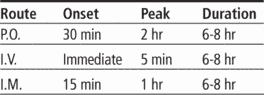
Adverse reactions
CNS: lethargy, hallucinations, anxiety, confusion, agitation, depression, fatigue, dizziness, seizures
CV: vein irritation, thrombophlebitis, heart failure
EENT: blurred vision, itchy eyes
GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, enterocolitis, gastritis, stomatitis, glossitis, black "hairy" tongue, furry tongue, oral or rectal candidiasis, pseudomembranous colitis
GU: vaginitis, nephropathy, interstitial nephritis
Hematologic: anemia, eosinophilia, agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia
Hepatic: nonspecific hepatitis
Musculoskeletal: arthritis exacerbation
Respiratory: wheezing, dyspnea, hypoxia, apnea
Skin: rash, urticaria, fever, diaphoresis
Other: pain at injection site, superinfections, hyperthermia, hypersensitivity reaction, anaphylaxis, serum sickness
Interactions
Drug-drug. Allopurinol: increased risk of rash
Chloramphenicol: synergistic or antagonistic effects
Hormonal contraceptives: decreased contraceptive effect, increased risk of breakthrough bleeding
Probenecid: decreased renal excretion of ampicillin, increased ampicillin blood level
Tetracyclines: reduced bactericidal effect
Drug-diagnostic tests. Conjugated estrone, estradiol, estriol-glucuronide, total conjugated estriols: increased levels in pregnant patients
Granulocytes, hemoglobin, platelets, white blood cells: decreased levels
Coombs' test, urine glucose: false-positive results
Eosinophils: increased count
Drug-food. Any food: reduced ampicillin efficacy
Patient monitoring
• Watch for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reaction.
☞ Monitor for seizures when giving high doses.
• Frequently measure patient's temperature and check for signs and symptoms of superinfection, especially oral or rectal candidiasis.
• Monitor for bleeding tendency or hemorrhage.
Patient teaching
• Tell patient to take oral dose with 8 oz of water 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal.
☞ Instruct patient to immediately report signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reaction, such as rash, fever, or chills.
• Inform patient that drug lowers resistance to certain other infections. Tell him to report new signs or symptoms of infection, especially in mouth or rectum.
• Advise patient to minimize GI upset by eating small, frequent servings of food and drinking plenty of fluids.
☞ Instruct patient to promptly report unusual bleeding or bruising.
• Tell patient to avoid activities that can cause injury. Advise him to use soft toothbrush and electric razor to avoid gum and skin injury.
• Inform patient taking hormonal contraceptives that drug may reduce contraceptive efficacy. Advise her to use alternative birth control method.
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, and foods mentioned above.