ovulation
[ov″u-la´shun]the discharge of a secondary oocyte from the graafian follicle; in an adult woman this normally occurs at intervals of about 28 days and alternates between the two ovaries. As a rule, only one secondary oocyte is produced, but occasionally ovulation produces two or more; if more than one subsequently become fertilized, the result may be multiple births, such as twins or triplets. adj., adj ov´ulatory.
Ovulation takes place approximately at the midpoint of the menstrual cycle, 14 days after the onset of menstruation. During the preceding weeks, a graafian follicle (cell cluster in the ovary containing the oocyte) grows from the size of a pinhead to that of a pea. At the moment of ovulation, the follicle bursts open and the ovum is discharged.
The discharged ovum enters the fallopian tube adjoining the ovary and moves toward the uterus; if it encounters a spermatozoon while it is still alive (about 48 hours), the two merge and fertilization takes place, usually in the fallopian tube. The fertilized ovum then makes its way to the uterus, where it becomes embedded in the prepared wall as the first stage of growth of the fetus (see illustration, and see also reproduction). If fertilization does not take place the ovum loses its vitality and the blood and tissue lining the uterus are shed in the menstrual flow.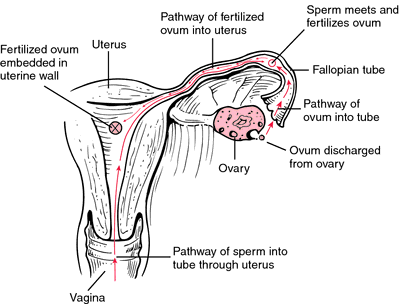
Ovulation takes place approximately at the midpoint of the menstrual cycle, 14 days after the onset of menstruation. During the preceding weeks, a graafian follicle (cell cluster in the ovary containing the oocyte) grows from the size of a pinhead to that of a pea. At the moment of ovulation, the follicle bursts open and the ovum is discharged.
The discharged ovum enters the fallopian tube adjoining the ovary and moves toward the uterus; if it encounters a spermatozoon while it is still alive (about 48 hours), the two merge and fertilization takes place, usually in the fallopian tube. The fertilized ovum then makes its way to the uterus, where it becomes embedded in the prepared wall as the first stage of growth of the fetus (see illustration, and see also reproduction). If fertilization does not take place the ovum loses its vitality and the blood and tissue lining the uterus are shed in the menstrual flow.

Ovulation.
ovulation method cervical mucus method; see discussion under contraception.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
ov·u·la·tion
(ov'yū-lā'shŭn, ō'vū-),Release of an ovum from the ovarian follicle.
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
o·vu·la·tion
(ov'yū-lā'shŭn)Release of an oocyte from the ovarian follicle.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
ovulation
The release of an OVUM from a mature Graafian follicle in the OVARY. Ovulation occurs about half way between the beginning of consecutive menstrual periods, usually about 14 days before the expected date of onset of the next period.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
ovulation
the bursting of the OVARIAN FOLLICLE (See also GRAAFIAN FOLLICLE on the surface of the ovary with the release of an egg which then normally passes into the OVIDUCT.Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
Ovulation
The phase of the female monthly cycle when a developed egg is released from the ovary into the fallopian tube for possible fertilization.
Mentioned in: Contraception, Dysmenorrhea, Emergency Contraception, Hormone Replacement Therapy, Infertility Therapies, Menopause, Ovarian Cysts, Recurrent Miscarriage
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
Patient discussion about Ovulation
Q. i just have my period last november 25 and ended on 28.when is my possible fertile and ovulation period please help me identify my fertile and ovulation period
A. If someone knew it, it'd solve the human race many problems with fertility. The problem is that ovulation (and thus, the period of possible fertility) happens 14 days BEFORE the onset of menses, so you know about it only retrospectively.
However there ways such as serial body temperature measuring, along with kits that measures the level of hormones in the urine in order to estimate the time of the coming ovulation, and help in timing intercourse.
You may read more about it here (www.mayoclinic.com/health/ovulation-signs/AN01521 ) but anyway, consulting a doctor (e.g. gynecologist) may be wise.
However there ways such as serial body temperature measuring, along with kits that measures the level of hormones in the urine in order to estimate the time of the coming ovulation, and help in timing intercourse.
You may read more about it here (www.mayoclinic.com/health/ovulation-signs/AN01521 ) but anyway, consulting a doctor (e.g. gynecologist) may be wise.
This content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms. The Questions and Answers are not endorsed or recommended and are made available by patients, not doctors.