syringe
[sir´inj, sĭ-rinj´]an instrument for introducing fluids into or withdrawing them from the body.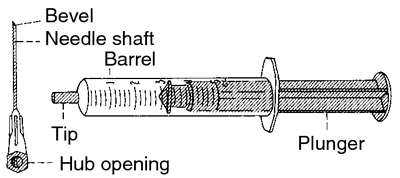

Components of a syringe. Shading indicates areas that must be kept sterile before and during parenteral injections. From Bolander, 1994.
Asepto syringe a syringe designed to fit directly into large lumen tubing; also used for intraoperative irrigation.
bulb syringe a syringe with a bulb on one end; compression of the bulb creates a vacuum for gentle suction of small amounts of bodily drainage, such as oral and nasal secretions. It is also used for intraoperative irrigation.

Using a bulb syringe. From Lammon et al., 1995.
hypodermic syringe one for introduction of liquids through a hollow needle into subcutaneous tissues.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
sy·ringe
(sĭ-rinj', sir'inj),An instrument used for injecting or withdrawing fluids, consisting of a barrel and plunger.
[G. syrinx, pipe or tube]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
syringe
(sə-rĭnj′, sîr′ĭnj)n.
1. A medical instrument used to inject fluids into the body or draw them from it.
2. A hypodermic syringe.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
syringe
A calibrated disposable plastic–or less commonly, a nondisposable glass tube with a rubber sealed plunger at one end and a tapered tip for the insertion of a needle at the other. See Electronic syringe, SofDraw™ safety syringe.McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
sy·ringe
(sir-inj')An instrument used for injecting or withdrawing fluids.
[G. syrinx, pipe or tube]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
syringe
An instrument, consisting of a barrel and a tight-fitting piston with a connecting rod, used to inject or withdraw fluid. The barrel is usually calibrated in fluid units and the nozzle is shaped to fit a standard range of needles. Luer-lock syringes are designed so that the needle cannot be forced off by high pressure. Most modern syringes are plastic and disposable and are pre-sterilized and supplied in sealed containers.Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005
sy·ringe
(sir-inj')An instrument used to inject or withdraw fluids, consisting of a barrel and plunger.
[G. syrinx, pipe or tube]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012