plane
[plān]1. a flat surface determined by the position of three points in space.
2. an imaginary flat surface that divides the body into sections (see accompanying figure). adj., adj pla´nar.
3. a specified level, as the plane of anesthesia.
4. to rub away or abrade; see also planing and plastic surgery.
5. a superficial incision in the wall of a cavity or between tissue layers, especially in plastic surgery, made so that the precise point of entry into the cavity or between the layers can be determined.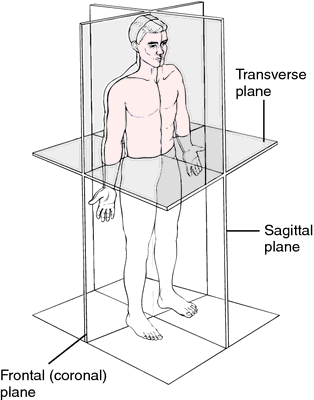

Planes of section. Transverse, sagittal, and frontal planes of the body. From Applegate, 2000.
coronal p's frontal p's.
datum plane a given horizontal plane from which craniometric measurements are made.
frontal p's those planes passing longitudinally through the body, an organ, or a part, at right angles to the median plane and dividing into front and back portions. Called also coronal planes.
horizontal plane transverse plane.
median plane one passing longitudinally through the body, an organ, or a part from front to back, dividing it into right and left halves.
sagittal p's vertical planes through the body parallel to the median plane or the sagittal suture, dividing the body into unequal left and right portions.
transverse plane one passing horizontally through the body, an organ, or a part at right angles to the median and frontal planes, dividing it into upper and lower portions. Called also horizontal plane.
vertical plane one perpendicular to a horizontal plane, such as a sagittal plane, median plane, or frontal plane.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
plane
(plān), [TA]1. A two-dimensional flat surface.
2. An imaginary surface formed by extension of a point through any axis or two definite points, in reference especially to craniometry and to pelvimetry.
Synonym(s): planum
[L. planus, flat]
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
plane
(plān) [TA]1. A flat surface.
See also: planum
See also: planum
2. An imaginary surface formed by extension through any axis or two definite points, in reference to pelvimetry and especially to craniometry.
[L. planus, flat]
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
plane
A flat surface.
aperture plane A plane that passes through the aperture of an optical system.
apparent frontoparallel plane (AFPP) Plane passing through the fixation point and containing all other points judged to appear in the same frontal plane. At about 1 metre from the eye it more or less coincides with a frontal plane; this is the abathic distance. Closer to 1 metre it is often a concave surface with its concavity turned towards the observer and beyond 1 metre it is a convex surface with its convexity turned towards the observer. See Hering-Hillebrand deviation; horopter.
cardinal plane's Planes, normal to the optical axis, which pass through the cardinal points of a lens or optical system. They are the focal planes, the nodal planes and the principal planes. (Sometimes, this definition also includes the object and image planes.) See cardinal points.
equatorial plane Vertical plane passing through the centre of curvature of the large circle of the eyeball, perpendicular to the optical axis and which divides the eyeball into anterior and posterior halves. See anterior segment of the eye; Listing's plane.
plane of fixation See plane of regard.
focal plane A plane, perpendicular to the optical axis, which passes through one of the focal points of an optical system. See principal focus.
frontal plane A vertical plane perpendicular to the median plane. When this plane passes through the centre of rotation of the eye it is called Listing's plane.
frontoparallel plane The frontal plane passing through the fixation point.
horizontal plane of the eye Plane, such as the xy plane, passing through the centre of rotation of the eye and dividing it into superior and inferior halves. When the eye is looking straight ahead this plane is horizontal. See subjective horizontal plane; xy plane.
image plane A plane, perpendicular to the optical axis at any axial image point of an optical system.
plane of incidence The plane containing the incident and reflected rays, and the normal to the surface at the point of incidence.
Listing's plane A frontal plane passing through the centre of rotation, which corresponds to the equatorial plane of the eye when it is looking in the straight-ahead position (Fig. P11).
median plane The vertical plane that divides the head into right and left halves.
plane mirror See plane mirror.
nodal plane A plane, perpendicular to the optical axis, which passes through one of the nodal points of an optical system (Fig. P12).
object plane A plane perpendicular to the optical axis at any axial object point of an optical system.
principal plane A plane perpendicular to the optical axis of an optical system at the point where the incident rays parallel to the optical axis intersect the refracted rays converging to the secondary focal point (secondary principal plane); or in which the refracted rays parallel to the optical axis intersect the incident rays coming from the primary focal point (primary principal plane). Each plane is an erect image of the other, and of the same size. For this reason they are sometimes also referred to as unit planes as they are conjugate planes in which the magnification is +1. In a thin lens these planes coincide at the lens (Fig. P12). See image distance; object distance; focal length; thin lens; nodal points; principal points; equivalent power.
plane of regard Plane containing the fixation point, the axes of fixation from the two eyes and the base line. Syn. plane of fixation.
sagittal plane A vertical plane parallel to the median plane as, for example, the yz plane.
spectacle plane A plane representing the orientation of the spectacle lenses relative to the eyes and passing through the posterior vertices of the two lenses. See pantoscopic angle; retroscopic angle; vertex distance.
subjective horizontal plane Plane fixed with respect to the eye, i.e. horizontal when the eye is in the primary position. See horizontal plane of the eye; primary position.
unit plane's See principal plane.
plane of vibration See polarized light.
visual plane The plane containing the two visual axes.
xy plane Horizontal plane of the eye containing both the x- and y-axes (Fig. P11). See anteroposterior axis; transverse axis.
yz plane Vertical plane of the eye containing both the y- and z-axes (Fig. P11). See anteroposterior axis; vertical axis.

aperture plane A plane that passes through the aperture of an optical system.
apparent frontoparallel plane (AFPP) Plane passing through the fixation point and containing all other points judged to appear in the same frontal plane. At about 1 metre from the eye it more or less coincides with a frontal plane; this is the abathic distance. Closer to 1 metre it is often a concave surface with its concavity turned towards the observer and beyond 1 metre it is a convex surface with its convexity turned towards the observer. See Hering-Hillebrand deviation; horopter.
cardinal plane's Planes, normal to the optical axis, which pass through the cardinal points of a lens or optical system. They are the focal planes, the nodal planes and the principal planes. (Sometimes, this definition also includes the object and image planes.) See cardinal points.
equatorial plane Vertical plane passing through the centre of curvature of the large circle of the eyeball, perpendicular to the optical axis and which divides the eyeball into anterior and posterior halves. See anterior segment of the eye; Listing's plane.
plane of fixation See plane of regard.
focal plane A plane, perpendicular to the optical axis, which passes through one of the focal points of an optical system. See principal focus.
frontal plane A vertical plane perpendicular to the median plane. When this plane passes through the centre of rotation of the eye it is called Listing's plane.
frontoparallel plane The frontal plane passing through the fixation point.
horizontal plane of the eye Plane, such as the xy plane, passing through the centre of rotation of the eye and dividing it into superior and inferior halves. When the eye is looking straight ahead this plane is horizontal. See subjective horizontal plane; xy plane.
image plane A plane, perpendicular to the optical axis at any axial image point of an optical system.
plane of incidence The plane containing the incident and reflected rays, and the normal to the surface at the point of incidence.
Listing's plane A frontal plane passing through the centre of rotation, which corresponds to the equatorial plane of the eye when it is looking in the straight-ahead position (Fig. P11).
median plane The vertical plane that divides the head into right and left halves.
plane mirror See plane mirror.
nodal plane A plane, perpendicular to the optical axis, which passes through one of the nodal points of an optical system (Fig. P12).
object plane A plane perpendicular to the optical axis at any axial object point of an optical system.
principal plane A plane perpendicular to the optical axis of an optical system at the point where the incident rays parallel to the optical axis intersect the refracted rays converging to the secondary focal point (secondary principal plane); or in which the refracted rays parallel to the optical axis intersect the incident rays coming from the primary focal point (primary principal plane). Each plane is an erect image of the other, and of the same size. For this reason they are sometimes also referred to as unit planes as they are conjugate planes in which the magnification is +1. In a thin lens these planes coincide at the lens (Fig. P12). See image distance; object distance; focal length; thin lens; nodal points; principal points; equivalent power.
plane of regard Plane containing the fixation point, the axes of fixation from the two eyes and the base line. Syn. plane of fixation.
sagittal plane A vertical plane parallel to the median plane as, for example, the yz plane.
spectacle plane A plane representing the orientation of the spectacle lenses relative to the eyes and passing through the posterior vertices of the two lenses. See pantoscopic angle; retroscopic angle; vertex distance.
subjective horizontal plane Plane fixed with respect to the eye, i.e. horizontal when the eye is in the primary position. See horizontal plane of the eye; primary position.
unit plane's See principal plane.
plane of vibration See polarized light.
visual plane The plane containing the two visual axes.
xy plane Horizontal plane of the eye containing both the x- and y-axes (Fig. P11). See anteroposterior axis; transverse axis.
yz plane Vertical plane of the eye containing both the y- and z-axes (Fig. P11). See anteroposterior axis; vertical axis.

Fig. P12 Primary and secondary principal planes HP and H′P′ of a thick lens in air (PF, anterior focal length; P′F′, posterior focal length; SF, front vertex focal length; S′F′, back vertex focal length; SF′1, back focal length of the first surface D1; S′F2, front focal length of the second surface D2; N and N′, nodal points)
Millodot: Dictionary of Optometry and Visual Science, 7th edition. © 2009 Butterworth-Heinemann
plane
(plān) [TA]1. Two-dimensional flat surface.
2. Imaginary surface formed by extension of a point through any axis or two definite points, in reference especially to craniometry and to pelvimetry.
[L. planus, flat]
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012
