base
[bās]1. the lowest part or foundation of anything. See also basis.
2. the main ingredient of a compound.
3. the nonacid part of a salt; a substance that combines with acids to form salts. In the chemical processes of the body, bases are essential to the maintenance of a normal acid-base balance. Excessive concentration of bases in the body fluids leads to alkalosis.
4. a unit of a removable dental prosthesis.
5. in genetics, a nucleotide, particularly one in a nucleic acid sequence.
intermediary base the layer of cement between a dental restoration and the tooth structure, acting as an insulator and protective barrier.
nitrogenous base an aromatic, nitrogen-containing molecule that serves as a proton acceptor, e.g., purine or pyrimidine.
ointment base a vehicle for the medicinal substances carried in an ointment.
purine b's a group of compounds of which purine is the base, including uric acid, adenine, xanthine, and theobromine. 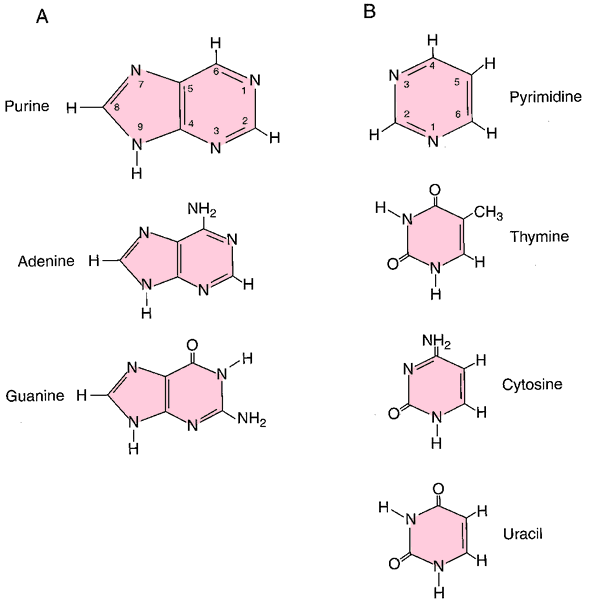

Bases. A, Purine and some substituted purine bases occurring in nucleic acids. B, Pyrimidine and some substituted pyrimidine bases occurring in nucleic acids. From Dorland's, 2000.
pyrimidine b's a group of chemical compounds of which pyrimidine is the base, including uracil, thymine, and cytosine, which are common constituents of nucleic acids.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
nitrogenous base
n.
Variant of nitrogen base.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
nitrogenous base
A molecule containing nitrogen with the chemical properties of a base.Nitrogenous bases—DNA
• Purine bases—Adenine (A), guanine (G).
• Pyrimidine bases—Cytosine (C), thymine (T).
Nitrogenous bases—RNA
• Purine bases—Adenine (A), guanine (G).
• Pyrimidine bases—Cytosine (C), uracil (U).
Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.