guanfacine
[gwahn´fah-sēn]guanfacine
Pharmacologic class: Centrally acting antiadrenergic
Therapeutic class: Antiadrenergic-sympatholytic, antihypertensive
Pregnancy risk category B
Action
Stimulates central alpha2-adrenergic receptors, reducing sympathetic nerve impulses from vasomotor center to heart and blood vessels
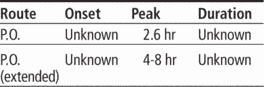
Availability
Tablets: 1 mg, 2 mg
Tablets (extended-release): 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, 4 mg
Indications and dosages
➣ Management of hypertension (used alone or in combination with other agents, especially thiazide diuretics)
Adults: 1 mg (immediate-release) P.O. at bedtime. If response unsatisfactory after 3 to 4 weeks, increase to 2 mg (immediate-release) P.O. at bedtime.
➣ Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) as monotherapy and as adjunctive therapy to stimulants
Adults and children age 6 and older: 1 mg (extended-release) P.O. daily; adjust in increments of no more than 1 mg/week. Maintain dosage within 1 to 4 mg/day, depending on clinical response and tolerability. Consider dosing on a mg/kg basis. Improvements have been observed starting at dosages of 0.05 to 0.08 mg/kg once daily. Dosages up to 0.12 mg/kg once daily may provide additional benefit. Dosages above 4 mg/day haven't been studied. If switching from immediate-release guanfacine, discontinue immediate-release treatment and titrate with extended-release, as directed.
Dosage adjustment
• Hepatic or renal impairment (immediate-release form)
• Concurrent use of CYP3A4 inducers such as rifampin (immediate-release form)
Off-label uses
• Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (immediate-release form)
• Treatment of heroin withdrawal
• Hypertension in pregnancy
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug, its components, or other products containing guanfacine
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• hepatic or renal impairment
• severe coronary insufficiency, cardiovascular or cerebovascular disease
• history of syncope, patients at risk for hypotension, bradycardia, heart block, or syncope, such as those taking antihypertensives (immediate-release form)
• concurrent use of CNS depressants
• concurrent use of antihypertensives, other products containing guanfacine, or CYP3A4/5 inhibitors such as ketoconazole (immediate-release form)
• elderly patients
• sedated patients (especially when given with centrally acting depressants)
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients
• children younger than age 6 (extended-release form) or 12 (immediate-release form).
Administration
• Measure heart rate and blood pressure before starting drug and after dosage increases.
• Give at bedtime to reduce daytime sleepiness (immediate-release form).
• Don't administer with high-fat meals (extended-release form).
• Know that therapy shouldn't be stopped abruptly, because this may cause rebound plasma and urinary catecholamines, anxiety, hypertension, and increase in blood pressure. When discontinuing, taper dosage in decrements of no more than 1 mg every 3 to 7 days.
• Be aware that drug may be used alone or with other agents, especially thiazide diuretics (immediate-release form).
• Be aware that for adolescents and children age 6 and older, efficacy beyond 9 weeks and safety beyond 2 years of treatment haven't been established.
• Don't substitute extended-release tablet for immediate-release tablet on a milligram-per-milligram basis, because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles.
Adverse reactions
CNS: somnolence, insomnia, dizziness, postural dizziness, lethargy, irritability, agitation, anxiety, nightmares, headache, fatigue, amnesia, confusion, depression, hypokinesia, asthenia, malaise, paresthesia, paresis, seizures
CV: hypertension, hypotension, syncope, bradycardia, palpitations, substernal pain, AV block, sinus arrhythmia
EENT: conjunctivitis, iritis, vision disturbance, tinnitus, rhinitis
GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, dysphagia, dry mouth
GU: erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, increased urinary frequency, enuresis
Musculoskeletal: leg cramps
Respiratory: dyspnea, asthma
Skin: dermatitis, pruritus, purpura, sweating, pallor, rash
Other: taste perversion, decreased appetite, weight gain, chest pain, hypersensitivity
Interactions
Drug-drug. Antihypertensives: increased risk of additive pharmacodynamic effects, such as hypotension and syncope
CNS depressants: (such as antipsychotics, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, sedative-hypnotics): additive sedation
CYP3A4 inducers (such as rifampin): decreased guanfacine plasma concentration
CYP3A4/5 inhibitors (such as ketoconazole), valproic acid: increased guanfacine plasma concentration
Phenobarbital, phenytoin: decreased elimination half-life and blood level of guanfacine
Valproic acid: increased serum valproic acid concentration
Drug-diagnostic tests. Alanine aminotransferase: increased level
Drug-food. High-fat meal: increased guanfacine Cmax and area under the curve
Drug-behaviors. Alcohol use: additive sedation
Patient monitoring
• Monitor patient for evidence of drug efficacy.
• Monitor patient closely during drug withdrawal.
☞ Continue to monitor heart rate and blood pressure periodically during therapy. Watch for hypotension, bradycardia, syncope, and heart block, especially in patients taking antihypertensives.
☞ Be aware that rash with exfoliation has occurred in a few patients. Should rash occur, discontinue drug and monitor patient appropriately.
Patient teaching
• Tell patient to take immediate-release tablets at bedtime to reduce daytime sleepiness.
• Tell patient to take extended-release tablets whole with water, milk, or other liquid but not to take with high-fat meals.
• Tell patient not to crush, chew, or break extended-release tablets before swallowing.
• Caution patient not to stop taking drug abruptly.
☞ Instruct patient how to recognize and immediately report signs and symptoms of serious cardiovascular disorders.
☞ Instruct patient to immediately report development of a rash.
• Advise patient to avoid driving and other hazardous activities until he knows how drug affects concentration and alertness.
• Tell patient to avoid alcohol during therapy.
• Advise patient to avoid dehydration or overheating.
• As appropriate, review all other significant adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, foods, and behaviors mentioned above.