abscess
[ab´ses]a localized collection of pus in a cavity formed by the disintegration of tissue. Abscesses are usually caused by specific microorganisms that invade the tissues, often by way of small wounds or breaks in the skin. An abscess is a natural defense mechanism in which the body attempts to localize an infection and wall off the microorganisms so that they cannot spread throughout the body. As the microorganisms destroy the tissue, an increased supply of blood is rushed to the area. The cells, bacteria, and dead tissue accumulate to form a clump of cream-colored liquid, which is the pus. The accumulating pus and the adjacent swollen, inflamed tissues press against the nerves, causing pain. The concentration of blood in the area causes redness. The abscess sometimes “comes to a head” by itself and breaks through the skin or other tissues, allowing the pus to drain. Local applications of heat may be used to facilitate localization and drainage. 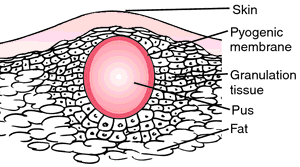

Abscess, cross section.
alveolar abscess a localized suppurative inflammation of tissues about the apex of the root of a tooth.
amebic abscess an abscess cavity of the liver resulting from liquefaction necrosis due to entrance of Entamoeba histolytica into the portal circulation in amebiasis; amebic abscesses may also affect the lungs, brain, and spleen.
Bartholin abscess acute infection of a Bartholin gland with symptoms including pain, swelling, cellulitis of the vulva, and dyspareunia. Treatment is incision and drainage of the abscess. Cultures should be obtained to rule out infections by Neisseria gonorrhoeae or Chlamydia.
Bezold's abscess one deep in the neck resulting from a complication of acute mastoiditis.
brain abscess see brain abscess.
Brodie's abscess a circumscribed abscess in bone, caused by hematogenous infection, that becomes a chronic nidus of infection.
cold abscess one of slow development and with little inflammation, usually tuberculous.
diffuse abscess an uncircumscribed abscess whose pus is diffused in the surrounding tissues.
gas abscess one containing gas, caused by gas-forming bacteria such as Clostridium perfringens. Called also Welch's abscess.
miliary abscess one composed of numerous small collections of pus.
pancreatic abscess one that occurs as a complication of acute pancreatitis or postoperative pancreatitis caused by secondary bacterial contamination.
perianal abscess one beneath the skin of the anus and the anal canal.
periapical abscess inflammation with pus in the tissues surrounding the apex of a tooth.
periodontal abscess a localized collection of pus in the periodontal tissue.
peritonsillar abscess a localized accumulation of pus in the peritonsillar tissue subsequent to suppurative inflammation of the tonsil; called also quinsy.
phlegmonous abscess one associated with acute inflammation of the subcutaneous connective tissue.
stitch abscess one developed about a stitch or suture.
thecal abscess one in the sheath of a tendon.
wandering abscess one that burrows into tissues and finally points at a distance from the site of origin.
Welch's abscess gas abscess.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
cold ab·scess
an abscess without heat or other usual signs of inflammation.
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
cold abscess
A well-circumscribed focus of acute inflammation without the usual signs of a 'hot' abscess–eg, calor, rubor, tumor, dolor–per Celsus; CAs 'classically' occur in paravertebral TB, and may be seen in normal persons infected by an attenuated organism, or in Pts with hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome given inadequate antibiotic therapy. See Job syndrome.McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
cold ab·scess
(kōld ab'ses)1. An abscess without heat or other usual signs of inflammation.
2. Synonym(s): tuberculous abscess.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012