boceprevir
Pharmacologic class: Hepatitis C NS3/4A protease inhibitor
Therapeutic class: Antiviral agent
Pregnancy risk category X
Action
Binds to the NS3 protease active site serine (S139) through an (alpha)-ketoamide functional group to inhibit viral replication in hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected host cells
Availability
Capsules: 200 mg
Indications and dosages
➣ Chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 in patients with compensated hepatic disease (including cirrhosis) who are previously untreated or who have failed previous interferon and ribavirin therapy
Adults age 18 and older: 800 mg P.O. t.i.d. (q 7 to 9 hours) in combination with peginterferon alfa and ribavirin; in patients with compensated cirrhosis, give peginterferon alfa and ribavirin for 4 weeks followed by 44 weeks boceprevir 800 mg t.i.d. (q 7 to 9 hours) in combination with peginterferon alfa and ribavirin
➣ Chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 in patients with compensated hepatic disease (without cirrhosis) who are previously untreated or are partial responders or relapsers to interferon and ribavirin therapy
Adults age 18 and older: Initiate therapy with peginterferon alfa and ribavirin for 4 weeks (treatment weeks 1 to 4). Add boceprevir 800 mg P.O. t.i.d. (q 7 to 9 hours) to peginterferon alfa and ribavirin regimen after 4 weeks of treatment. Based on patient's HCV-RNA levels at treatment week 8, treatment week 12, and treatment week 24, use the following response-guided therapy guidelines below to determine duration of treatment.
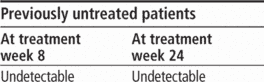
Complete three-drug regimen at treatment week 28.
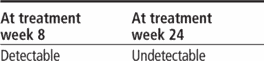
Continue all three drugs and finish through treatment week 36; then give peginterferon alfa and ribavirin and finish through treatment week 48.
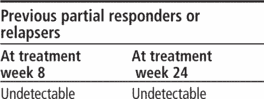
Complete three-drug regimen at treatment week 36.

Continue all three drugs and finish through treatment week 36; then give peginterferon alfa and ribavirin and finish through treatment week 48.
Treatment futility
If the patient has HCV-RNA results of 100 international units/ml or greater at treatment week 12, discontinue three-drug regimen. If the patient has confirmed, detectable HCV-RNA at treatment week 24, discontinue three-drug regimen.
Contraindications
• Contraindications to peginterferon alfa and ribavirin (because boceprevir must be administered with these drugs)
• Concurrent use of drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A4/5 for clearance, and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious or life-threatening events, including cisapride (not available in the United States), alfuzosin, dihydroergotamine, drospirenone, ergonovine, ergotamine, lovastatin, methylergonovine, oral midazolam, pimozide, sildenafil (Revatio) and tadalafil (Adcirca) when used for pulmonary arterial hypertension, simvastatin, and triazolam
• Concurrent use of potent CYP3A4/5 inducers when significantly reduced boceprevir plasma concentrations may be associated with reduced efficacy, including carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampin, and St. John's wort
• Pregnancy and in men whose female partners are pregnant
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• patients with anemia or neutropenia
• patients with decompensated cirrhosis or organ transplant, co-infection with HCV and HIV, or hepatitis B virus
• patients with hepatic or renal impairment (avoid use)
• concurrent use of antidepressants such as trazodone, desipramine, or sedatives-hypnotics such as alprazolam and I.V. midazolam (requires close monitoring and consideration of dosage reduction of these drugs)
• concurrent use of antifungals (dosages of ketoconazole and itraconazole shouldn't exceed 200 mg/day if given with boceprevir)
• concurrent use of colchicine for gout flares, prophylaxis for gout flares, or familial Mediterranean fever (requires dosage reduction)
• concurrent use of rifabutin (not recommended)
• concurrent use of dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, such as felodipine, nifedipine, and nicardipine (clinical monitoring recommended)
• concurrent use of dexamethasone (avoid use if possible or use with caution if use is necessary)
• concurrent use of inhaled corticosteroids budesonide, fluticasone (avoid use if possible, particularly for extended durations)
• concurrent use of bosentan (monitor patient closely)
• concurrent use of HIV non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors such as efavirenz (avoid use)
• concurrent use of atazanavir/ritonavir, darunavir/ritonavir, or lopinavir/ritonavir combinations (not recommended)
• concurrent use of ritonavir
• concurrent use of atorvastatin (requires careful titration; atorvastatin dose not to exceed 20 mg daily)
• concurrent use of salmeterol (not recommended)
• concurrent use of methadone or buprenorphine (clinical monitoring recommended; may require altered methadone or buprenorphine dosage)
• concurrent use of sildenafil, tadalafil, or vardenafil when used for erectile dysfunction (don't exceed recommended reduced dosages of these drugs)
• elderly patients
• breastfeeding patients
• children (safety and efficacy not established).
Administration
• Administer with food (a meal or light snack).
☞ Don't administer boceprevir without peginterferon alfa and ribavirin. Drug must not be used as monotherapy.
• Obtain CBC with WBC differential in all patients before starting drug. Be aware that decreased hemoglobin level or neutrophil count may require a decrease in dosage, interruption, or discontinuation of peginterferon alfa or ribavirin.
• Because this drug is given with ribavirin, ensure that a negative pregnancy test has been obtained immediately before starting therapy.
• Be aware that the Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry is available to monitor maternal-fetal outcomes of pregnancies in female patients and female partners of male patients exposed to ribavirin during treatment and for 6 months after treatment cessation.
• Be aware that boceprevir dosage reduction isn't recommended. If the patient has a serious adverse reaction potentially related to peginterferon alfa or ribavirin, the peginterferon alfa or ribavirin dosage should be reduced or discontinued.
Adverse reactions
CNS: fatigue, headache, asthenia, dizziness, insomnia, irritability
GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dry mouth
Hematologic: anemia, neutropenia
Musculoskeletal: arthralgia
Respiratory: exertional dyspnea
Skin: alopecia, dry skin, rash
Other: chills, dysgeusia, decreased appetite
Interactions
Drug-drug. Alpha1-adrenoreceptors (alfuzosin): increased alfuzosin concentration, resulting in hypotension
Antiarrhythmics (amiodarone, bepridil [not available in the United States], flecainide, propafenone, quinidine): increased antiarrhythmic concentration with risk of serious or life-threatening adverse events
Anticoagulants (warfarin): altered warfarin concentration
Anticonvulsants (carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin), antimycobacterials (rifampin): possible loss of virologic response to boceprevir
Antidepressants (desipramine, trazodone): increased trazodone and desipramine plasma concentrations, resulting in increased adverse reactions, such as dizziness, hypotension, and syncope
Antifungals (itraconazole, ketoconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole): increased plasma concentrations of these drugs
Antigout drugs (colchicine): significantly increased colchicine level, resulting in possible fatal toxicity
Anti-infectives (clarithromycin): increased clarithromycin concentration
Antimycobacterials (rifabutin): increased risk of rifabutin exposure and decreased risk of boceprevir exposure
Beta-agonists, inhaled (salmeterol): increased risk of salmeterol-associated CV events
Corticosteroids, inhaled (budesonide, fluticasone): increased budesonide and fluticasone plasma concentrations, resulting in significantly reduced serum cortisol concentration
Corticosteroids, systemic (dexamethasone): decreased boceprevir plasma concentration, with possible loss of boceprevir therapeutic effect
Digoxin: increased digoxin concentration, with risk of toxicity
Dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (felodipine, nicardipine, nifedipine): increased dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker plasma concentration
Endothelin receptor antagonists (bosentan): increased bosentan concentration
Ergot derivatives (dihydroergotamine, ergonovine, ergotamine, methyler-gonovine): increased risk of acute ergot toxicity characterized by peripheral vasospasm and ischemia of extremities and other tissues
GI motility agents (cisapride, not available in the United States): increased risk of cardiac arrhythmias
HIV non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (efavirenz): decreased boceprevir plasma trough concentration, resulting in loss of boceprevir therapeutic effect
HIV protease inhibitor combinations (atazanavir/ritonavir): reduced steady-state exposure to atazanavir and ritonavir
HIV protease inhibitor combinations (darunavir/ritonavir, lopinavir/ritonavir): reduced steady-state exposure to boceprevir, darunavir, lopinavir, and ritonavir
HIV protease inhibitors (ritonavir): decreased boceprevir concentration HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (atorvastatin): increased atorvastatin concentration
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (lovastatin, simvastatin): increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis
Immunosuppressants (cyclosporine, sirolimus, tacrolimus): significantly increased cyclosporine, sirolimus, and tacrolimus plasma concentrations
Neuroleptics (pimozide): increased risk of cardiac arrhythmias
Opioid analgesics (buprenorphine, methadone): possible increased or decreased methadone or buprenorphine plasma concentration
Oral contraceptives (drospirenone): increased risk of hyperkalemia
Oral contraceptives (drospirenone, ethinyl estradiol): increased drospirenone and decreased ethinyl estradiol concentrations (effect on other progestins is unknown but increases in exposure are anticipated)
Phosphodiesterase type 5 enzyme inhibitors (sildenafil, tadalafil) when used for pulmonary arterial hypertension: increased risk of PDE5 inhibitor-associated adverse events, including visual abnormalities, hypotension, prolonged erection, and syncope
Phosphodiesterase type 5 enzyme inhibitors (sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil) when used for erectile dysfunction: increased sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil levels, resulting in increased adverse reactions
Sedative-hypnotics (alprazolam, I.V. midazolam): increased concentrations of alprazolam and midazolam, with risk of respiratory depression or prolonged sedation
Sedative-hypnotics (triazolam, oral midazolam): prolonged or increased sedation or respiratory depression
Drug-diagnostic tests. Hemoglobin, neutrophils, platelets: decreased levels
Drug-food. Any food: enhanced boceprevir exposure
Drug-herbs. St. John's wort: possible loss of virologic response to boceprevir
Patient monitoring
• Continue to monitor CBC with WBC differential at treatment weeks 4, 8, and 12; closely monitor at other times as clinically appropriate.
• Monitor HCV-RNA levels at treatment weeks 4, 8, 12, and 24, at the end of treatment, during treatment follow-up, and at other times as clinically indicated. Be aware that discontinuation of therapy is recommended in all patients with HCV-RNA level of 100 international units/ml or greater at treatment week 12 or confirmed detectable HCV-RNA level at treatment week 24.
• If patient is also receiving antiarrhythmics, bosentan, calcium channel blockers, digoxin, immunosuppressants, or opioid analgesics, monitor therapeutic levels of these drugs.
• Monitor INR closely if patient is receiving warfarin while taking this three-drug combination.
• Closely watch for adverse reactions in patients taking erectile dysfunction drugs while also taking this three-drug combination.
• Closely watch for respiratory depression or prolonged sedation in patients also taking sedatives or hypnotics with this three-drug combination.
Patient teaching
• Tell patient to take drug with food (a meal or light snack).
☞ Advise patient that boceprevir must not be used alone, because of the high probability of resistance without combination anti-HCV therapies.
• Tell patient that if he misses a dose and it's less than 2 hours before the next dose is due, he should skip the missed dose. If he misses a dose and it's 2 or more hours before the next dose is due, he should take the missed dose and then resume the normal dosing schedule.
• Tell patient that laboratory evaluations are required before starting therapy and periodically thereafter.
• Inform female patient that she must have a negative pregnancy test before starting therapy and monthly thereafter during therapy.
• Advise female patient of childbearing age and female partners of male patients to avoid pregnancy during therapy with this three-drug combination by practicing effective contraception with at least two forms of contraceptives during therapy and for 6 months after therapy ends. Tell female patient not to rely on efficacy of systemic hormonal contraceptives during this treatment. Two alternative effective methods of contraception include intrauterine devices and barrier methods.
• Tell female patient of childbearing age that breastfeeding isn't recommended during therapy.
• Instruct patient to tell prescriber about all drugs and herbal products he's taking, because many drugs and some herbs have the potential for serious drug interactions and shouldn't be taken with boceprevir.
• Inform patient that it isn't known how treatment of hepatitis C virus infection affects transmission and that appropriate precautions to prevent transmission of hepatitis C virus should be taken.
• As appropriate, review all other significant adverse reactions and interactions, especially those related to the drugs, tests, food, and herbs mentioned above.