megacolon
[meg″ah-ko´lon]dilatation and hypertrophy of the colon.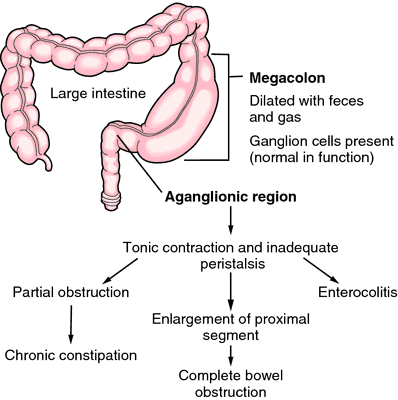

Megacolon. From McKinney et al., 2000
acquired megacolon colonic enlargement associated with chronic constipation, but with normal ganglion cell innervation.
acute megacolon toxic megacolon.
aganglionic megacolon (congenital megacolon) Hirschsprung's disease.
toxic megacolon acute dilatation of the colon associated with amebic dysentery or ulcerative colitis; called also acute megacolon.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
ac·quired meg·a·co·lon
megacolon occurring in association with an acquired disease; occurs in inflammatory bowel disease (toxic megacolon) and Chagas disease (South American trypanosomiasis).
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
megacolon
A massively distended colon with ↓ activity, due to defective innervation–congenital, intraluminal overgrowth of microorganisms or of psychogenic origin Clinical Intestinal obstruction, constipation, vomiting, abdominal distension, poor weight gain, retarded growth Management Temporary colostomy for bowel rest, followed by resection of affected bowel segment Prognosis Sx eliminated in ± 90% of Pts with surgery; outcomes better with early intervention Megacolon
Congenital megacolon Congenital aganglionosis, Hirschsprung's disease A disease affecting 1:5000 live births, with a sibling risk of 1% for girls and 5% for boys; Hirschsprung's disease–HD is ten-fold more common in Down syndrome; other anomalies in HD include hydrocephalus, VSD, cryptorchism, diverticulosis of the urinary bladder, renal cysts and agenesis, polyposis coli, Laurence-Moon-Biedl syndrome Treatment Resection of aganglionic colon
Acquired megacolon A condition related to narcotics or disruption of ganglionic innervation–eg idiopathic hypomotility, neuropathies–parkinsonism, multiple sclerosis, myotonic dystrophy, diabetic neuropathy, Chagas' disease, smooth muscle disorders–amyloidosis and progressive systemic sclerosis and metabolic disease–hypokalemia, lead poisoning, porphyria, pheochromocytoma, hypothyroidism and may be due to intraluminal overgrowth of microorganisms in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis–toxic megacolon–characterized by mucosal necrosis, transmural inflammation and systemic 'toxicity' associated with high fever, tachycardia, leukocytosis and diarrhea; in psychogenic megacolon, no radiologic or pathologic defects are present–the condition may be related to a 'fixation' in Freud's anal retentive stage of psychosexual development, with constipation of later onset than in HD, possibly 2º to abuse of anthracine laxatives
McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
ac·quired meg·a·co·lon
(ă-kwīrd megă-kō-lŏn)Megacolon associated with disease; occurs in inflammatory bowel disease and Chagas disease.
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012