beclomethasone dipropionate
Pharmacologic class: Corticosteroid
Therapeutic class: Anti-inflammatory agent
Pregnancy risk category C
Action
Unclear. May decrease inflammation by stabilizing leukocytic lysosomal membrane, decreasing number and activity of inflammatory cells, inhibiting bronchoconstriction (leading to direct smooth muscle relaxation), and reducing airway hyperresponsiveness.
Availability
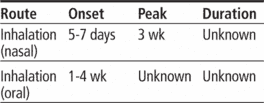
Inhalation aerosol: 40-mcg metered inhalation in 7.3-g canister; 80-mcg metered inhalation in 7.3-g canister
Inhalation capsules: 100 mcg, 200 mcg
Nasal spray: 0.042% (25-g bottle containing 180 metered inhalations)
Indications and dosages
➣ Maintenance treatment of asthma as prophylaxis; asthma patients who require systemic steroids for whom adding an inhaled steroid may reduce or eliminate the need for systemic steroids
Adults and children ages 12 and older: When previous therapy was bronchodilator alone, 40 to 80 mcg by oral inhalation (QVAR) b.i.d.; maximum of 320 mcg b.i.d. When previous therapy was inhaled steroid, 40 to 160 mcg by oral inhalation (QVAR) b.i.d.; maximum of 320 mcg b.i.d.
Children ages 5 to 11: When previous therapy was bronchodilator alone, 40 mcg by oral inhalation (QVAR) b.i.d.; maximum of 80 mcg b.i.d. When previous therapy was inhaled steroid, 40 mcg by oral inhalation (QVAR) b.i.d.; maximum of 80 mcg b.i.d.
➣ Seasonal or perennial rhinitis
Adults and children ages 12 and older: One or two inhalations (42 to 84 mcg Beconase AQ Nasal Spray) in each nostril b.i.d.
Children ages 6 to 12: One inhalation (42 mcg Beconase AQ Nasal Spray) in each nostril b.i.d.
Contraindications
• Hypersensitivity to drug
• Status asthmaticus
Precautions
Use cautiously in:
• active untreated infections, diabetes mellitus, glaucoma, underlying immunosuppression
• patients receiving concurrent systemic corticosteroids
• pregnant or breastfeeding patients
• children younger than age 6.
Administration
• Use spacer device to ensure proper delivery of dose and to help prevent candidiasis and hoarseness.
• After inhalation, tell patient to hold his breath for a few seconds before exhaling.
• For greater efficacy, wait 1 minute between inhalations.
• If patient is also receiving a bronchodilator, administer it at least 15 minutes before beclomethasone.
• Discontinue drug after 3 weeks if symptoms don't improve markedly.
Adverse reactions
CNS: headache
EENT: cataracts, nasal irritation or congestion, epistaxis, perforated nasal septum, nasopharyngeal or oropharyngeal fungal infections, hoarseness, throat irritation
GI: esophageal candidiasis
Metabolic: adrenal suppression Respiratory: cough, wheezing, bronchospasm
Skin: urticaria, angioedema
Other: anosmia, Churg-Strauss syndrome, hypersensitivity reactions
Interactions
None significant
Patient monitoring
• Assess patient's mouth daily for signs of fungal infection.
• Observe patient for proper inhaler use.
Patient teaching
• Instruct patient to hold inhaled drug in airway for several seconds before exhaling and to wait 1 minute between inhalations.
• Advise patient to rinse mouth after using inhaler and to wash and dry inhaler thoroughly to help prevent fungal infections and sore throat.
• Encourage patient to document use of drug and his response in a diary.
• If patient is also using a bronchodilator, teach him to use it at least 15 minutes before beclomethasone.
• As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions.