oxidation
[ok″sĭ-da´shun]the act of oxidizing or state of being oxidized. Chemically it consists of the increase of positive charges on an atom or the loss of negative charges. Univalent oxidation indicates loss of one electron; divalent oxidation, the loss of two electrons. The opposite reaction to oxidation is reduction. adj., adj ox´idative.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
ox·i·da·tion
(ok'si-dā'shŭn),1. Combination with oxygen.
2. Increasing the valence of an atom or ion by the loss from it of hydrogen or of one or more electrons thus rendering it more electropositive, as when iron is changed from the ferrous (2+) to the ferric (3+) state.
3. In bacteriology, the aerobic dissimilation of substrates with the production of energy and water; in contrast to fermentation, the transfer of electrons in the oxidation process is accomplished through the respiratory chain, which uses oxygen as the final electron acceptor.
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
oxidation
The combination of a molecule with oxygen, which increases the atom’s valence with the loss of a hydrogen ion or one or more electrons. Oxidation reactions commonly involve the combination with oxygen free radicals, and result in major organ damage that accumulates with time; they are implicated in age-related damage, degenerative phenomena and cancer, and may be ameliorated with antioxidants, including vitamin C, vitamin E, glutathione and superoxide dismutase.Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. All rights reserved.
ox·i·da·tion
(ok'si-dā'shŭn)1. Combination with oxygen; increasing the valence of an atom or ion by the loss from it of hydrogen or of one or more electrons.
2. bacteriology The aerobic dissimilation of substrates with the production of energy and water; the transfer of electrons is accomplished through the respiratory chain, which uses oxygen as the final electron acceptor.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
oxidation
- the addition of oxygen to a substance to increase the proportion of oxygen in its molecule. Oxidation can be achieved without oxygen by the removal of hydrogen (dehydrogenation).
- any reaction involving loss of electrons from an atom. For example,
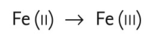
Collins Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
Oxidation
When a chemical element or compound loses an electron.
Mentioned in: Methemoglobinemia
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
ox·i·da·tion
(ok'si-dā'shŭn)Combination with oxygen; increasing the valence of an atom or ion by the loss from it of hydrogen or of one or more electrons.
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012