artery
[ahr´ter-e]a vessel through which the blood passes away from the heart to various parts of the body. The wall of an artery consists typically of an outer coat (tunica adventitia), a middle coat (tunica media), and an inner coat (tunica intima). 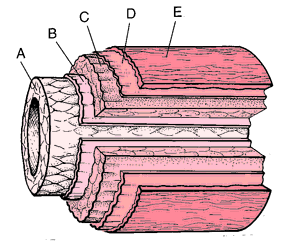 For names of specific arteries, see anatomic Table of Arteries in Appendices. See also Plate 8.
For names of specific arteries, see anatomic Table of Arteries in Appendices. See also Plate 8.

Representation of arterial coats: A, tunica intima; B, internal elastic lamina; C, tunica media; D, external elastic lamina; E, tunica externa. From Dorland's, 2000.
end artery one that undergoes progressive branching without development of channels connecting with other arteries.
nutrient artery any artery that supplies the marrow, or medulla, of a long bone.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
nu·tri·ent ar·ter·y
[TA]an artery of variable origin that supplies the medullary cavity of a long bone.
Synonym(s): arteria nutricia [TA], nutrient vessel
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
nu·tri·ent ar·te·ry
(nū'trē-ĕnt ahr'tĕr-ē) [TA]An artery of variable origin that supplies the medullary cavity of a long bone.
Synonym(s): arteria nutricia [TA] , nutrient vessel.
Synonym(s): arteria nutricia [TA] , nutrient vessel.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012